Figure 4.
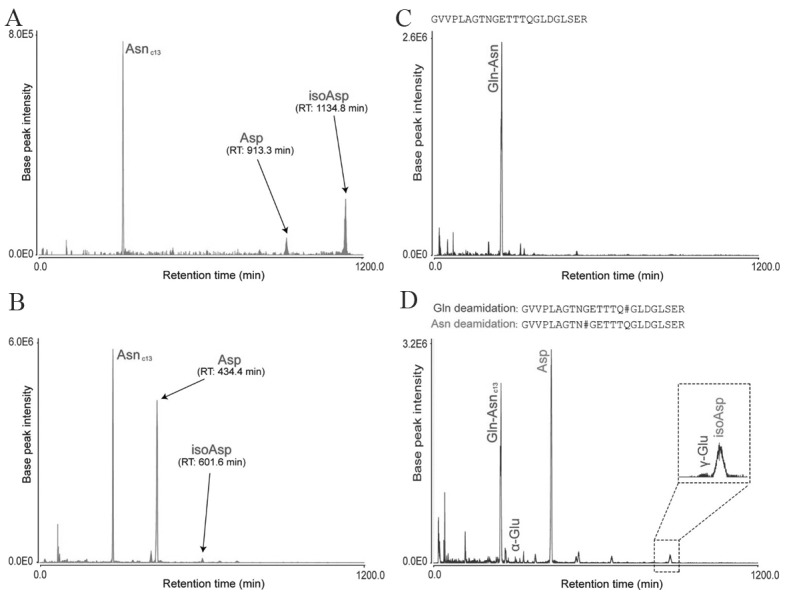
Separation of Asn and Gln deamidation peptides from trypsin-digested human brain tissue using LERLIC-MS/MS. (Adopted from Serra et al.[233]) A) Extracted ion chromatograms of peptide N#GFDQCDYGWLSDASVR showing separated triad of Asn deamidated peptides B) Extracted ion chromatograms of VDKGVVPLAGTN#GETTTQGLDGLSER peptide showing separation of carbon-13 peak of nondeamidated peptide (AsnC13), Asp (aspartyl isomer) and isoaspartyl isomer (isoAsn), C) Extracted ion chromatograms of GVVPLAGTNGETTTQGLDGLSER nondeamidated peptide, D) Extracted ion chromatograms of two deamidated proteoforms with asn and Gln deamidated residues in peptide GVVPLAGTN#GETTTQGLDGLSER and GVVPLAGTNGETTTQ#GLDGLSER where Gln-Asnc13 is a carbon-13 peak of the nondeamidated peptide; α-Glu is α-glutamyl isomer; Asp is Asp aspartyl isomer; γ-Glu is γ-glutamyl isomer; and isoAsp reamin isoaspartyl isomer. #indicates site of modification.
