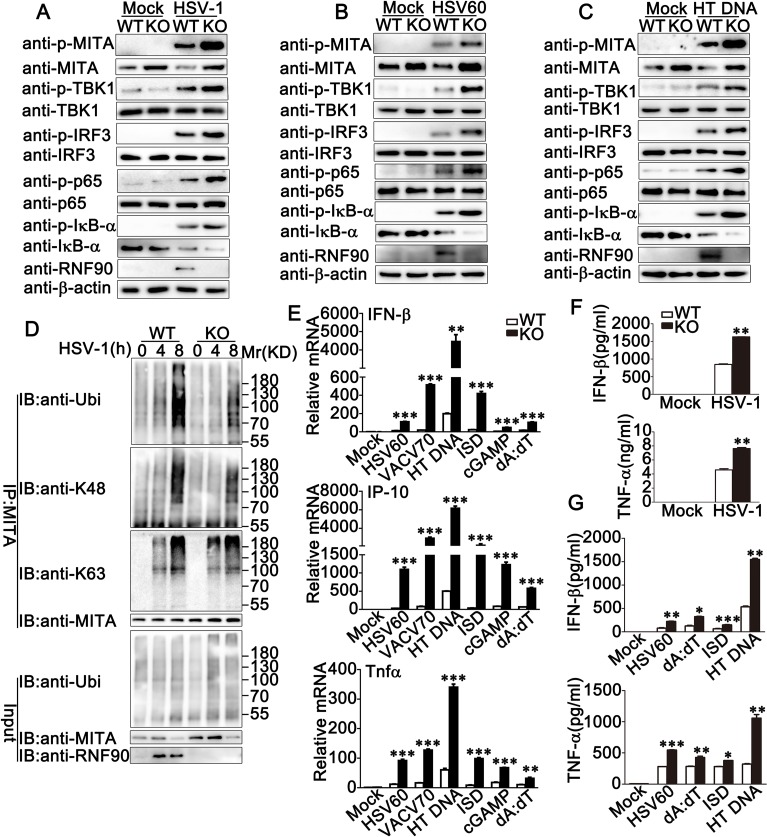
Fig 6. RNF90 deficiency promotes exogenous cytosolic DNA-triggered innate immune responses in BMDCs.
(A) Wild-type (WT) and RNF90-deficient (KO) BMDCs were infected with HSV-1 for 8 h. The cells were lysed for immunoblot analysis. (B, C) Wild-type (WT) and RNF90-deficient (KO) BMDCs were transfected with 1 μg/ml HSV60 (B) or 1 μg/ml HT DNA (C) for 8 h. The cells were lysed for immunoblot analysis. (D) Wild-type (WT) and RNF90-deficient (KO) BMDCs were infected with HSV-1 for indicated periods of time. The cells were lysed for immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblot (IB) assays. (E) Wild-type (WT) and RNF90-deficient (KO) BMDCs were transfected with HSV60 (1 μg/ml), VACV70 (1 μg/ml), HT DNA (1 μg/ml), ISD (1 μg/ml), cGAMP (1 μg/ml) and poly(dA:dT) (1 μg/ml) separately for 8 h. The cells were lysed for real-time PCR analysis. (F) Wild-type (WT) and RNF90-deficient (KO) BMDCs were infected with HSV-1 for 24 h. The supernatants were collected and subjected to ELISA analysis. (G) Wild-type (WT) and RNF90-deficient (KO) BMDCs were transfected with HSV60 (1 μg/ml), poly(dA:dT) (1 μg/ml), ISD (1 μg/ml), and HT DNA (1 μg/ml) separately for 24 h. The supernatants were collected and subjected to ELISA analysis. β-actin served as a loading control in all the immunoblot assays. The data are representative of three independent experiments and are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.