Fig. 2. Schematic of the experimental setup.
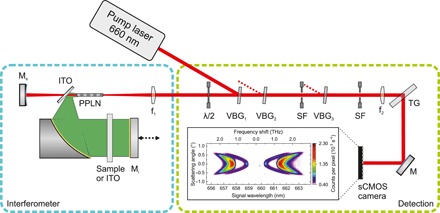
A continuous-wave laser with a wavelength of 659.58 nm is reflected by a VBG (VBG1) into the interferometer part of the setup through a zero-order half-wave plate (λ/2) controlling the polarization. It is then focused by a lens f1 into a periodically poled 1-mm-long MgO-doped LiNbO3 (PPLN) crystal generating signal and terahertz photons that are separated by an ITO. Signal and pump radiation are reflected at Ms directly into the crystal. The terahertz radiation passes the object twice, being reflected by a moveable mirror Mi. In the second traverse of the pump through the PPLN, additional signal and idler photons are generated. Afterward, the lens f1 collimates the pump and signal radiation for the detection starting with filtering the pump radiation by three VBGs and spatial filters (SF). To obtain the frequency-angular spectrum, the signal radiation is focused through a transmission grating (TG) by the lens f2 onto a sCMOS camera. The inset shows a frequency-angular spectrum for the used crystal (poling period Λ = 90 μm, pumped with 450 mW). The scattering angle corresponds to the angle after the transmission from the crystal to air.
