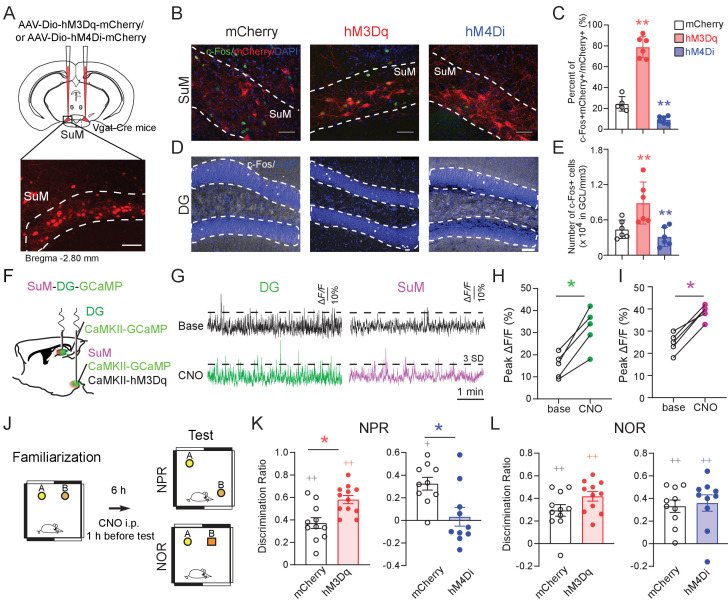
Figure 2. SuM activity is required for spatial memory retrieval.
(A) Experimental scheme. Coronal sections showing mCherry expression in SuMLVgat neurons in Vgat-Cre mice. Scale bar = 100 µm. (B) Sample images showing the c-Fos expression in SuMLVgat neurons 1 hr after CNO injection from AAV-DIO-hM3Dq- and AAV-DIO-hM4Di- injected mice. Scale bar = 100 µm. (C) Quantification of the density of c-Fos+/mCherry+ SuM neurons. CNO 1 mg/kg induced higher density of c-Fos+/hM3Dq-mCherry+ cells, but lower density of c-Fos+/hM4Di-mCherry+ cells. (n = 5–6 mice, one-way ANOVA followed by PLSD post hoc test, **p < 0.01). (D) Sample images showing c-Fos expression in the DG 1 hr after CNO injection from AAV-DIO-hM3Dq- and AAV-DIO-hM4Di- injected mice. Scale bar = 100 µm. (E) Quantification of c-Fos expression in DG GCs. C-Fos+ GCs were increased in hM3Dq-mice, but decreased in hM4Di-mice 1 hr after CNO injection. GCL: granule cell layer. (n = 5–6 mice, one-way ANOVA followed by PLSD post hoc test, **p < 0.01). (F) Diagram of in vivo photometry recording. AAV-CaMKII-GCaMP6f was injected in the left DG, and AAV-CaMKII-GCaMP6f mixed with CaMKII-hM3Dq was injected in the left SuM. Optic fibers were implanted above the DG and SuM, respectively. (G) Typical GCaMP6f traces (5 min) of baseline (upper) and 40 mins after 1 mg/kg CNO injection (below) from the DG and SuM. (H) The peak ∆F/F of the DG calcium signal increased after CNO injection. (n = 5 mice, paired t-test, t = 6.126, *p < 0.05). (I) The peak of ∆F/F of the SuM calcium signal increased after CNO injection. (n = 5 mice, paired t-test, t = 9.037, *p < 0.05). (J) Diagram of the NPR and NOR tests. CNO (1 mg/kg) was administrated 1 hr before these tests. (K) Activation or inhibition of SuMVgat neurons increased or decreased the discrimination ratio in the NPR test, respectively. (Unpaired t-test, t21 = 2.244, *p = 0.0358 in hM3Dq-mice, t18 = 2.238, *p = 0.0381 in hM4Di-mice). (L) Activation or inhibition of SuMVgat neurons did not change the discrimination ratio in the NOR test. (Unpaired t-test, t21 = 1.869, p > 0.05 in hM3Dq-mice, t18 = 0.9197, p > 0.05 in hM4Di-mice).