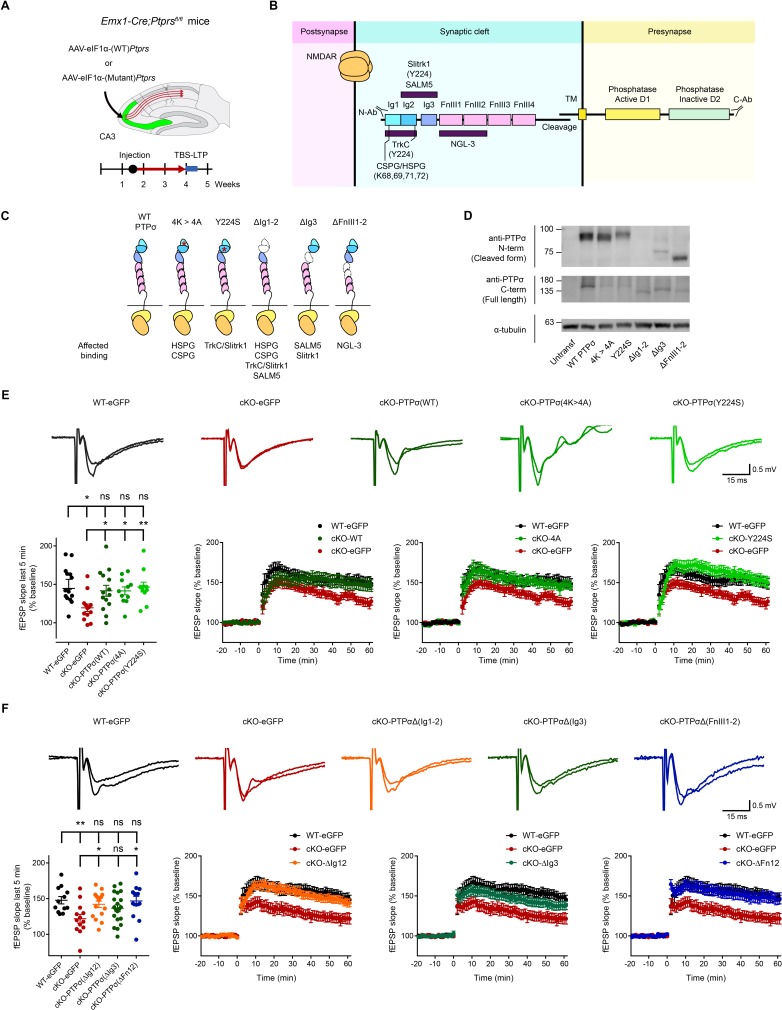
Figure 3. Re-expression of presynaptic PTP σ rescues postsynaptic LTP in the hippocampus through mechanisms independent of the extracellular region of PTPσ.
(A) Diagram depicting re-expression of WT and mutant PTPσ proteins in the CA3 region of the hippocampus by local injection of AAV(php.eB)-eIF1a-Ptprs (WT and mutants), followed by measurement of TBS-LTP. (B) Diagram depicting the domain structures of PTPσ and extracellular and cytoplasmic regions/domains involved in protein-protein interactions or tyrosine phosphatase activity. The first three Ig domains are important for trans-synaptic adhesions with Slitrk1, TrkC, CSPG/HSPG or SALM5, and the residues Y224 and K68/K69/K71/K72 are important for Slitrk1 and CSPG/HSPG interactions, respectively. (C) Specific PTPσ mutants used in our experiments, with point mutations or small deletions in the extracellular domains. All binding partners of PTPσ affected by the mutations/deletions are also indicated. (D) Expression levels and sizes of PTPσ mutants, revealed by immunoblot analysis of HEK293T cell lysates using two independent PTPσ antibodies targeting the N-terminal region (~Ig1-2) and C-terminus (last 30 residues) that can detect all PTPσ mutants, except for PTPσ-ΔIg12, which is not detected by the N-terminal antibody. (E) Rescue of TBS-LTP at SC-CA1 synapses by re-expression of WT PTPσ as well as mutant PTPσ (lacking CSPG/HSPG and Slitrk1 interactions) in the CA3 region of Emx1-Cre;Ptprsfl/fl mice (P28–32) through local injection of AAV-eIF1a-Ptprs-WT/mut. In control experiments, AAV-hSyn-eGFP was injected into the CA3 region of both Ptprsfl/fl (WT) and Emx1-Cre;Ptprsfl/fl mice. (n = 14 slices from four mice [WT-eGFP], 13, 5 [cKO-eGFP], 14, 6 [cKO-PTPσ-WT], 11, 4 [cKO-PTPσ−4A], and 11, 4 [cKO-PTPσ-Y224S], *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ns, not significant, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test). (F) Full and partial rescue of TBS-LTP at SC-CA1 synapses by re-expression of mutant PTPσ lacking Ig1+2 (ΔIg12), Ig3 (ΔIg3), or FNIII1+2 (ΔFN12) domains in the CA3 region of Emx1-Cre;Ptprsfl/fl mice (P28–32) by local injection of AAV-eEF1-Ptprs. Note that expression of PTPσ-ΔIg3 induces a partial rescue. Control virus (AAV-eIF1a-eGFP) was injected into the CA3 region of both Ptprsfl/fl (control) and Emx1-Cre;Ptprsfl/fl mice. (n = 12 slices from four mice [WT-eGFP], 13, 4 [cKO-eGFP], 16, 5 [cKO-PTPσ-ΔIg12], 20, 6 [cKO-PTPσ-ΔIg3], and 13, 5 [cKO-PTPσ-ΔFn12], *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ns, not significant, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test).