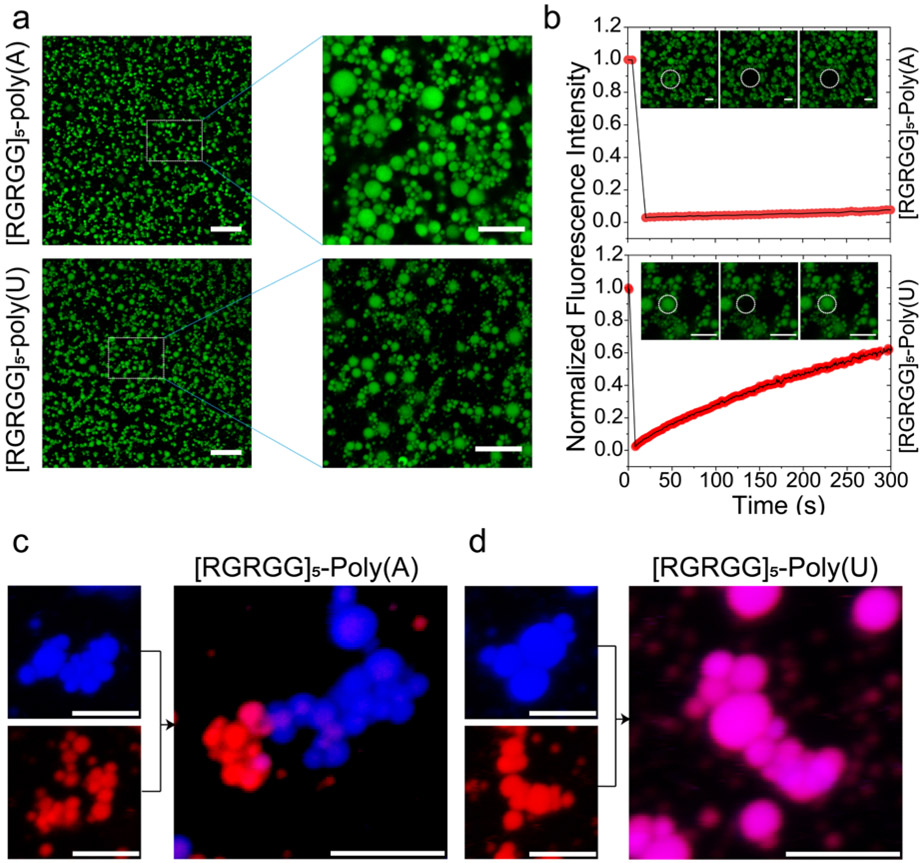
Figure 6: Long-range ionic repulsion competes with short-range attraction at high RNA-to-peptide ratio leading to a colloid-like cluster phase:
a) Fluorescence micrographs showing cluster formation for [RGRGG]5-poly(A) (top) and [RGRGG]5-poly(U) condensates (bottom). Scale bar represents 20 μm (left) and 10 μm (right). b) RNA sequence tunes the fluid dynamics of [RGRGG]5 clusters showing arrested diffusion in poly(A) clusters and a more dynamic diffusion in poly(U) clusters as evidenced by the fluorescence recovery time traces. Scale bars represent 5 μm for poly(A) images and 4 μm for poly(U) images. Corresponding movies are provided as Supplementary Movies 8 and 9. c) [RGRGG]5-poly(A) condensates can form co-clusters that retain their composition in a complex mixture. d) The [RGRGG]5-poly(U) condensates exchange their content rapidly under similar conditions. Scale bar represents 5 μm for both (c) and (d).