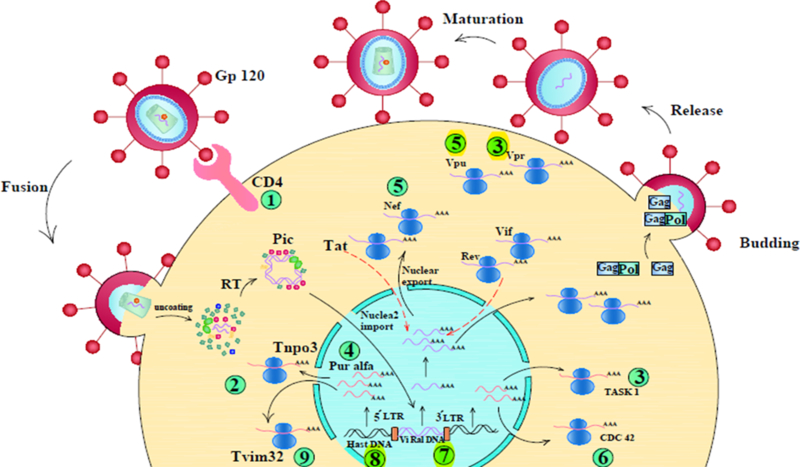
Figure 2. A schematic of microRNA networks affected by HIV virus.
(1) Up-regulation of miR-221 & 222 blocks CD4 receptor and inhibits entry of virus into the cell. (2) Up-regulation of miR-128 represses nuclear import of the virus. (3) Down regulation of miR-34a enhances release of virus and increases vpu activity. (4) Up-regulation of miR-20a decreases tat activity, inhibits binding of pur α to the LTR promoter, and represses virus replication in monocytes. (5) Up-regulation of miR-223 represses nef, vpr and blocks apoptosis in non-infected CD4 T-cells; miR-n367 decreases nef protein and virus virulence. (6) Down-regulation of miR-29 a/b increases cdc42 expression and promotes apoptosis in CD4 T-cells, (7) Up-regulation of miR-H3 interacts with the tata box in 5́ LTR, enhances promoter activity and increases RNA transcription and protein expression. (8) Up-regulation of miR-TaR3p decreases virus replication via targeting the TaR element in the 5́ LTR. (9) Up-regulation of miR-155 maintains the virus in the latent phase and reduces Nf-κβ signaling pathway