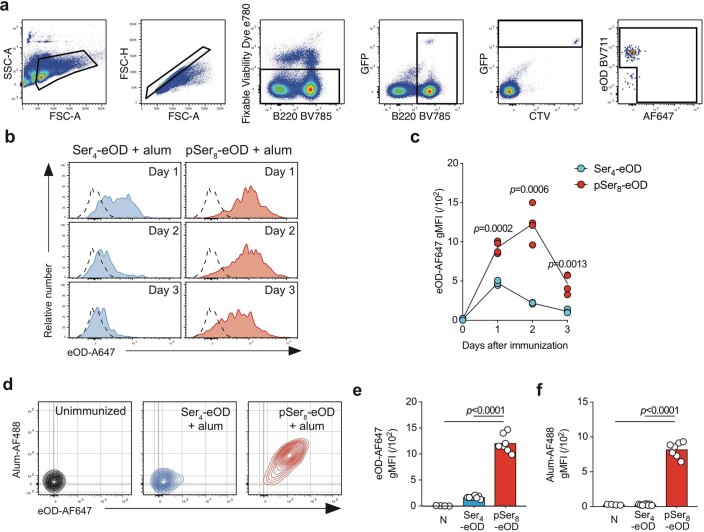
Extended Data Fig. 5. VRC01gHL cells take up eOD bound to alum particles in vivo.
(a) Gating strategy used to identify GFP+ VRC01gHL B cells. In vivo-acquired eOD antigen had been labeled with AF647 prior to injection. B cells were additionally stained ex vivo with BV711-labeled eOD to further confirm the specificity of the donor cells. (b, c) C57BL/6 mice adoptively transferred with 1x106 GFP+ CTV+ VRC01gHL B cells were immunized by i.p. injection of 5 µg AF647-labelled Ser4-eOD-GT8 or pSer8-eOD-GT8 together with 1 mg alum. (b) Representative flow cytometry analysis of VRC01gHL B cells. (c) Quantitation of antigen uptake over time. Lines indicate the mean. Data are representative of two independent experiments, n = 3 mice for d1/2 Ser4-eOD-GT8, n = 4 mice for d3 Ser4-eOD-GT8 and d1-3 pSer8-eOD-GT8. Statistical analysis was performed using Two-tailed Student t-test. (d–f) C57BL/6 mice adoptively transferred with 1x106 CTV+ VRC01gHL B cells were immunized by i.p. injection of 5 µg AF647-labelled Ser4-eOD-GT8 or pSer8-eOD-GT8 together with 1 mg pSer-AF488 labelled alum. (d) Representative flow cytometry plot of VRC0gHL cells. (e) Quantification of eOD-GT8 uptake by VRC01gHL cells. (f) Quantification of alum uptake by VRC0gHL cells. Bars represent the mean. Data combined from two independent experiments, n = 4 mice for unimmunized, n = 8 mice for Ser4-eOD-GT8 + alum, n = 7 mice for pSer8-eOD-GT8 + alum. Statistical analysis was performed using One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test.