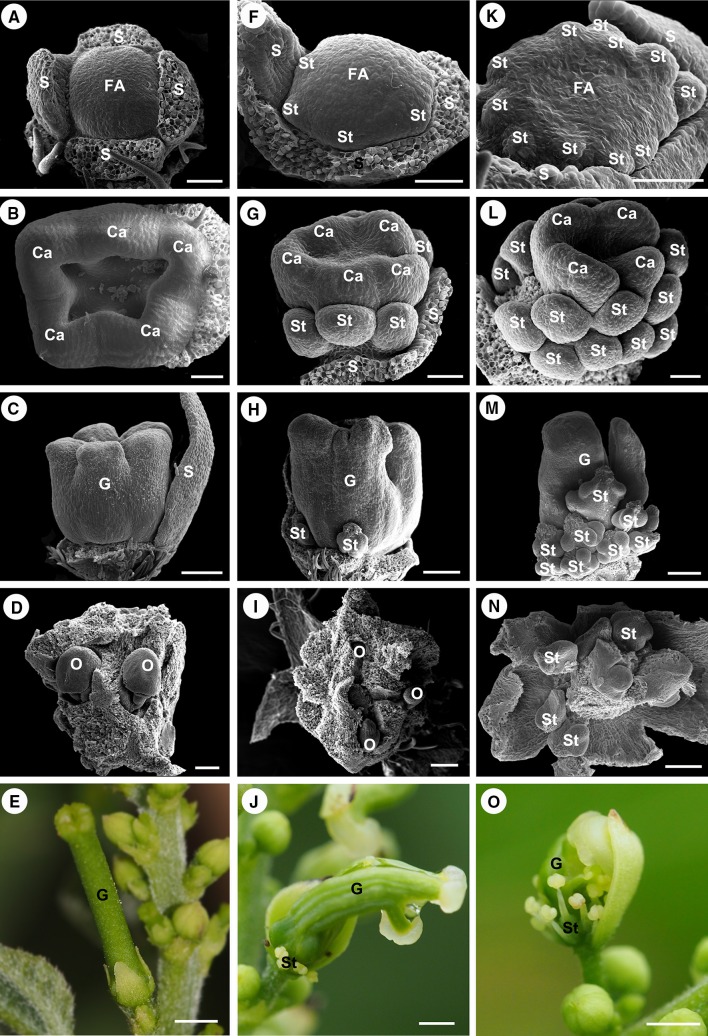
Fig. 8.
Three patterns of flower development in BA-treated male flower meristem in Plukenetia volubilis. a–e Normal female flower development in treated flower meristem; a a flat floral apex is formed; b the carpel primordia are initiated; c the gynoecium primordium is formed; d the developed ovules in the ovary; e a normal female flower is formed; f–j hermaphroditic flower development in treated flower meristem; f a few stamen primordia are initiated at the base of floral apex; g the carpel primordia are initiated at the central of floral meristem; h the gynoecium primordium is formed with stamens at the base; i the developed ovules in the ovary; j a hermaphroditic flower is formed with fertile stamens and pistil. k–o Abnormal hermaphroditic flower development in treated flower meristem; k numerous stamen primordia are initiated; l the carpel primordia are initiated at the central of floral meristem; m an abnormal gynoecium is formed with numerous stamens at the base; n no ovules found in the ovary; o an abnormal hermaphroditic flower is formed with fertile stamens. Abbreviations: FA, floral apex; S, sepal primordium; Ca, Carpel primordium; St, stamen primordia; G, gynoecium primordium. Scale bar: (a, b, f, g, k, l) = 50 µm; (d, i, n) = 100 µm; (c, h, m) = 200 µm; (e) = 2 mm; (j, o) = 5 mm