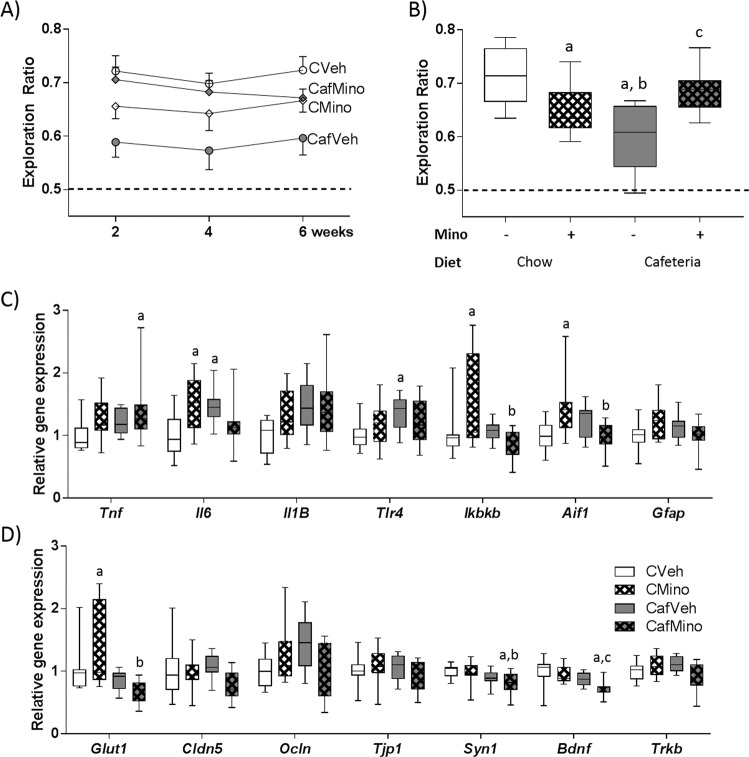
Fig. 2. Minocycline treatment improves spatial recognition memory and hippocampal pro-inflammatory gene expression in cafeteria-fed rats.
a Novel place task performance over the study and b average place task performance expressed as exploration ratios. Relative gene expression of c pro-inflammatory signals and d markers for blood brain barrier integrity, synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis in the dorsal hippocampus. Aif1 allograft inflammatory factor 1, Bdnf brain derived neurotrophic factor, Cldn5 claudin 5, Gfap glial fibrillary acidic protein, Glut1 glucose transporter 1, Ikbkb inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase subunit beta, Il6 interleukin-6, Il1B interleukin-Iβ, Ocln occludin, Syn1 synapsin 1, Tlr4 toll-like receptor 4, Tjp1 tight junction protein 1, Tnf tumor necrosis factor a, Trkb tropomyosin receptor kinase. Data expressed as box-and-whisker plots (min, IQR, max); n = 11–12; data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey-adjusted post hoc testing. ap < 0.05 relative to CVeh, bp < 0.05 relative to CMino, cp < 0.05 relative to CafVeh.