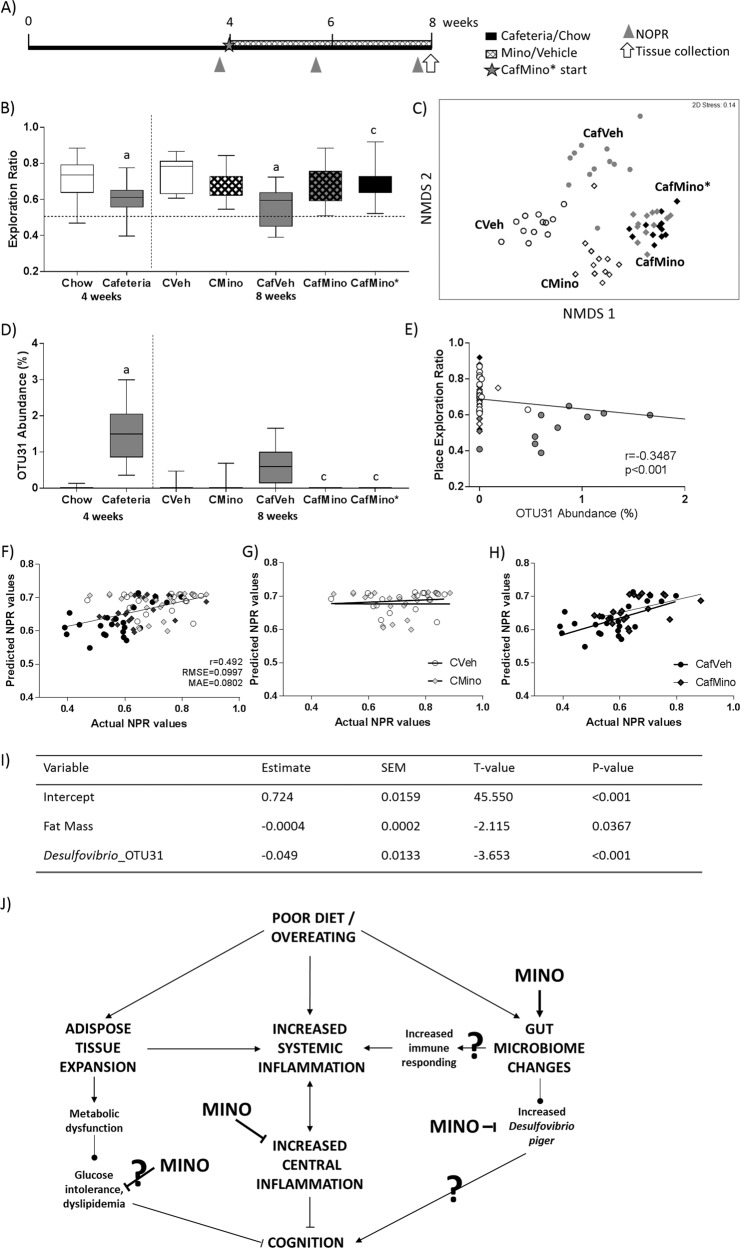
Fig. 4. Impact of minocycline treatment following 4 weeks of cafeteria diet on place task performance, fat mass and microbiota.
a Study timeline. b Average novel place task performance post-minocycline treatment expressed as exploration ratios. Data expressed as box-and-whisker plots (min, IQR, max); n = 11–12; data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey-adjusted post hoc testing. ap < 0.05 relative to CVeh, bp < 0.05 relative to CMino, cp < 0.05 relative to CafVeh. c Nonmetric multidimensional scaling (Bray–Curtis, 1000 permutations) showing similarity between fecal microbiota samples at 8 weeks. d Relative abundance of OTU31 at 4 and 8 weeks. Data expressed as box-and-whisker plots (min, IQR, max); analyzed using Kruskal–Wallis test followed by nonparametric Dunn–Bonferroni post hoc testing. ap < 0.05 relative to Chow at 4 weeks, cp < 0.05 relative to CafVeh at 8 weeks. e Scatterplot of Pearson correlation between place exploration ratio and relative OTU31 abundance, showing overall line of best fit; n = 10–12. o Vehicle-treated animals (open: chow, gray: cafeteria); ◊: minocycline treated animals (open: chow, gray: cafeteria, black: CafMino*). f Prediction of place task performance using final multiple regression model overall and for g chow-fed and h cafeteria-fed rats. i Final multiple regression model based on body composition and OTUs of interest. Training dataset: 112 observations from N = 60 rats. Test dataset: n = 89 observations from N = 48 rats. r correlation coefficient, RMSE root mean square error, MAE mean absolute error. CafMino* represents a replication group for the previous study, where rats were placed on both cafeteria diet and minocycline when all other rats were allocated to vehicle or minocycline. j Poor diet and overeating lead to increased adiposity and systemic low-grade inflammation, as well as altered gut microbiota. Systemic inflammation is highly interrelated with central inflammatory tone, which was inhibited by minocycline treatment. Changes to the gut microbiome include altered composition, which may contribute to the diet-induced state of systemic inflammation. Cafeteria diet enriched Desulfovibrio piger which was depleted by minocycline and negatively associated with place task performance in both experiments. Minocycline treatment improved short-term spatial recognition memory, measured by the novel place recognition task. Pointed arrow: promotion of the downstream process; blunted arrow: inhibition of the downstream process.?: hypothesized mechanism.