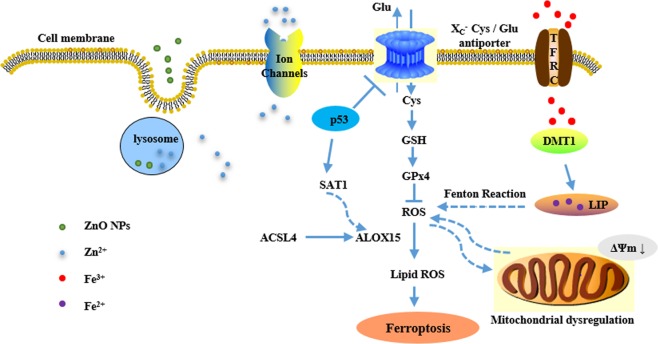
Fig. 7. Proposed mechanism of ZnO NPs-induced ferroptosis.
Ferroptosis is initiated via various signal pathways, such as Fe2+ accumulation, glutathione depletion and lipid peroxidation. The ZnO NPs can be endocytosed into lysosomal compartments where ZnO dissolves and releases zinc ions into the cytoplasm. ZnO NPs and zinc ions in the cytoplasm can activate p53, which may repress the transcription of SLC7A11, a component of the cystine/glutamate antiporter and glutathione depletion, and trigger SAT1 gene expression is enhanced in the presence of activated p53. Similarly, ZnO NPs and zinc ions in the cytoplasm can also impair organelles such as mitochondria and disrupting iron metabolism. and subsequent ferroptosis can occur by over-accumulation of lipid ROS.