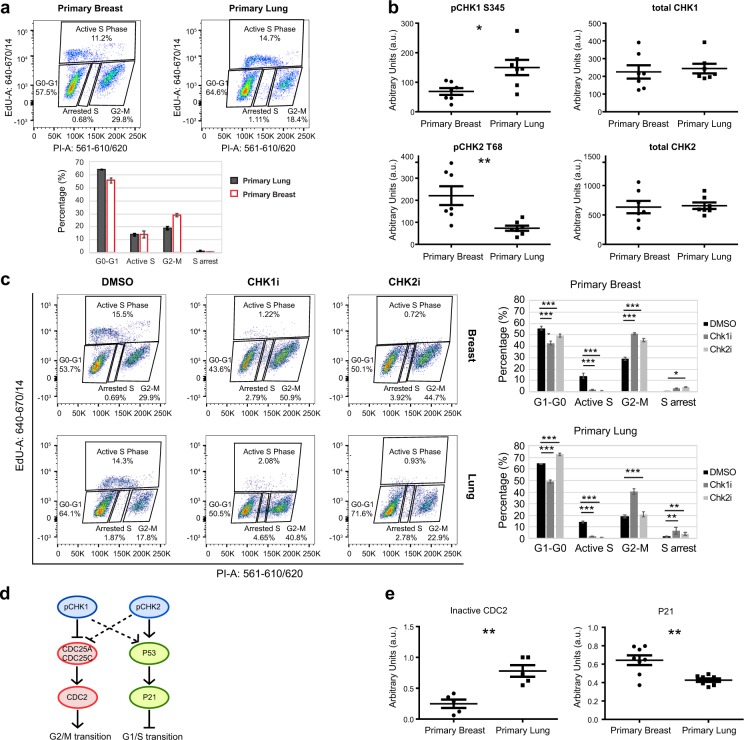
Fig. 1. CHK1 and CHK2 dynamics are associated with differential cell cycle regulation in human primary breast and lung cells.
a Cell cycle profile of human primary breast and lung cells. The results of three independent replicates are depicted (details are available in Supplementary Material). Error bars represent the standard deviation. b Expression analysis of total and active CHK1 and CHK2. Lysates from seven primary breast samples and seven primary lung samples, which were isolated from different batches at different times, were analyzed on western blot (Supplementary Fig. 1) and quantified as described in Supplementary Material. A two-sided t test was performed to compare the protein levels between primary breast and lung cells. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. c CHK1 inhibition distorts the cell cycle profile of both lung and breast cells, whereas an effect of CHK2 inhibition is predominantly observed in breast cells. Cells were treated with DMSO, CHK1 (PF477736, Sigma-Aldrich #PZ0186; 1 µM), or CHK2 inhibitor (Cayman Chemicals #17552; 10 µM) for 16 h. During the last 2 h, cells were incubated in the presence of 10 μM EdU. Depicted is a representative experiment (three independent replicates, error bars represent the standard deviation). A two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test was performed to compare CHK1- and CHK2-inhibited samples with the DMSO-treated control (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). d CHK1 and CHK2 have partially overlapping functions in regulating the cell cycle. Depicted is a cartoon model of regulation of P53, P21, CDC25, and CDC2 by CHK1 and CHK2. CHK1 and CHK2 have overlapping targets, but CHK2 is considered to have a larger role in inducing P53 phosphorylation and P21 activation. CHK1 and CHK2 can both inactivate CDC25C, but CHK1 is considered to be the main inhibitor of CDC25A. CDC25A and CDC25C are phosphatases for CDC2, which remove inhibitory phosphorylation residues, resulting in CDC2 activity and G2-M transition. e Differential activity of CHK1 and CHK2 in breast and lung cells is reflected in P21 levels and CDC2 activity. P21 levels are higher in breast cells, whereas inactive CDC2 levels (pCDC2 Y15) are higher in lung cells (details are available in Supplementary Material). A two-sided t test was performed to compare the protein levels between breast and lung cells. **p < 0.01.