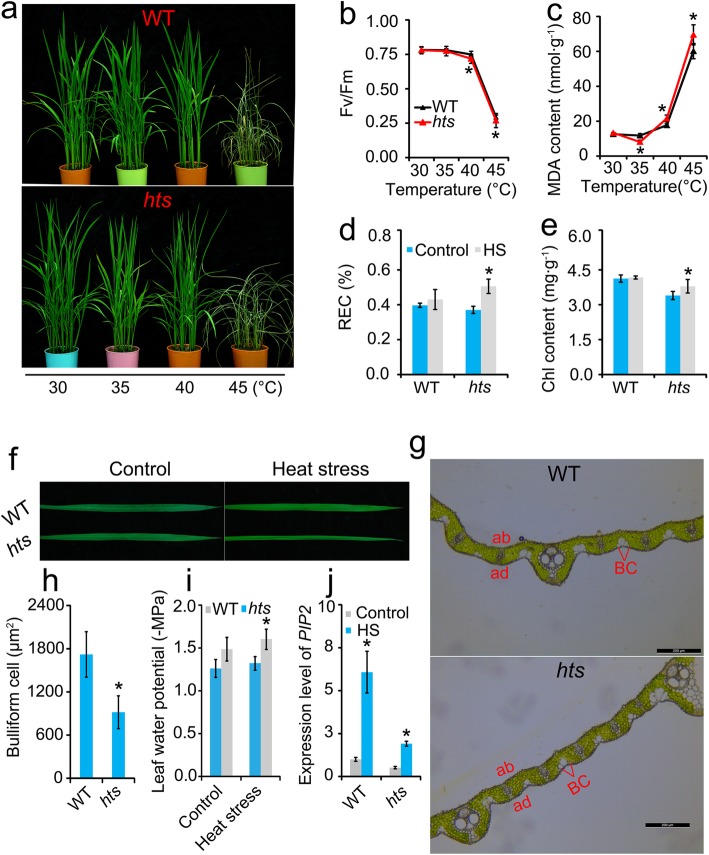
Fig. 1.
Responses of rice plants to different temperatures under heat stress conditions. a Photographs of WT and hts plants under different temperature conditions; b Fv/Fm; c, MDA; d, Relative ion leakage; e, Chlorophyll content. f, Photographs of leaf morphology under control and heat stress conditions; g, Photographs of bullioform cell in leaf of WT and hts plants under control condition. ‘ad’ stands for adaxial and ‘ab’ for abaxial, ‘BC’ for bulliform cells; h, Mean value of area of bulliform cell; i, Relative leaf water potential; j, Expression levels of PIP2. Vertical bars denote standard deviations (n = 3). A t-test was conducted to compare the difference between control and heat stress within a cultivar on the same day. * denotes P < 0.05