Figure 6.
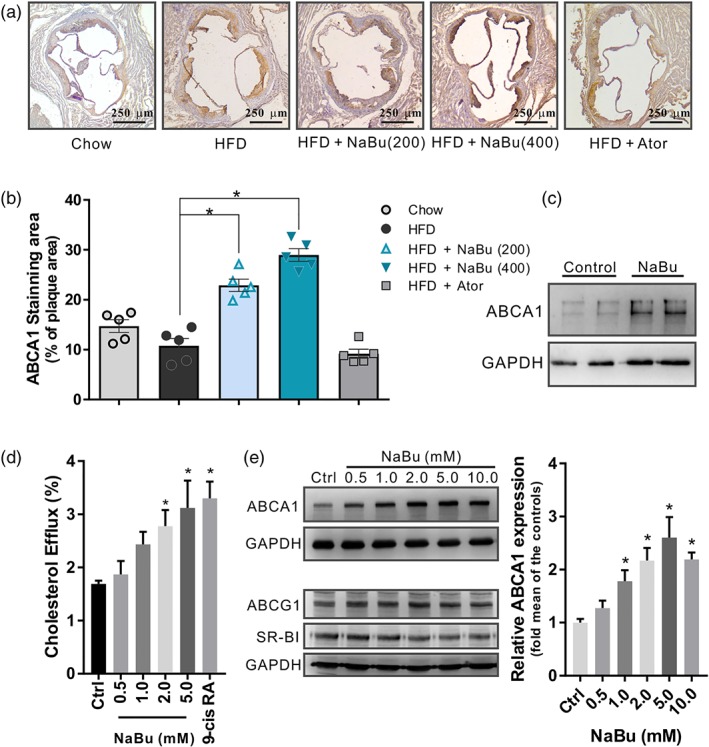
Effect of butyrate on ABCA1 induction in vivo and in vitro. (a) Representative immunohistochemistry sections and (b) quantitative analysis of ABCA1‐positive area (% of plaque area) in the lesions of aortic sinus, data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 5). (c) Western blot analysis of the ABCA1 levels in butyrate‐treated peritoneal macrophages from C57BL6/J mice (n = 4 per group). (d) [3H]‐Cholesterol efflux induced by butyrate was evaluated by incubating with ApoA‐I (10 μg·ml−1) in RAW 264.7 macrophages and calculated as a percentage of the radioactivity in the supernatant to the total radioactivity in the supernatant and cell lysates, 9‐cis RA: 9‐cis retinoic acid 10 μmol·L−1 (n = 5). (e) Western blots of ABCA1, ABCG1, and SR‐BI with corresponding quantifications in RAW 264.7 macrophages incubated with indicated butyrate for 24 hr (n = 5). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM, * represent significance versus vehicle control (Ctrl)
