Figure 2.
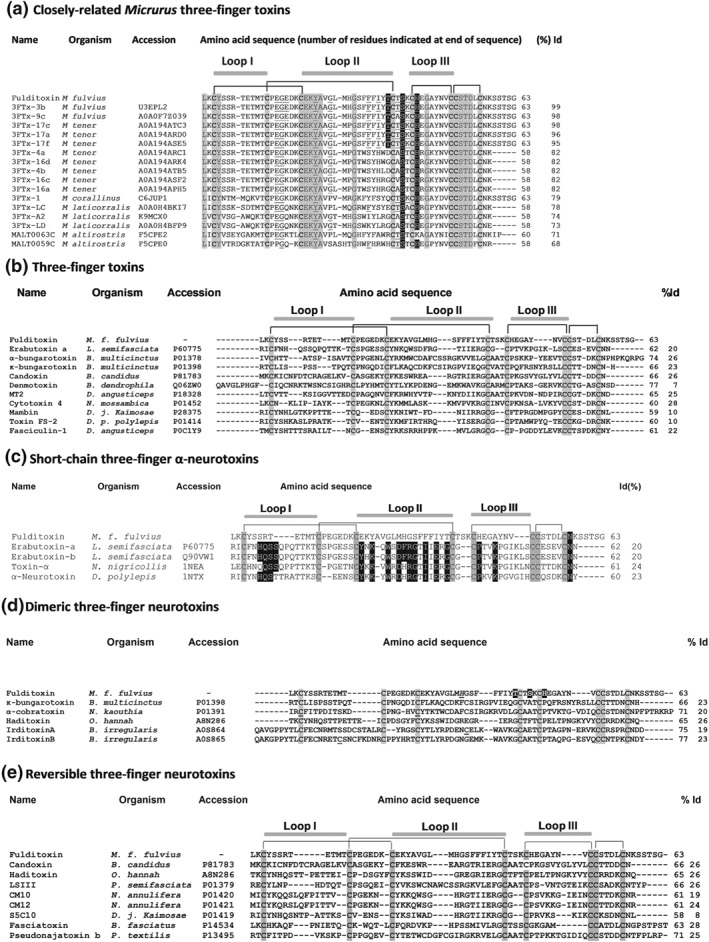
Comparison of the amino acid sequence of fulditoxin with sequences other snake three‐finger toxins. In all panels, the accession numbers and the source organism are indicated. Only the conserved cysteine residues within each group are shaded in grey. The number of amino acid (AA) residues and the percentage identity (% Id) of the respective toxins with fulditoxin is indicated at the end. The disulfide linkages and segments contributing to the three loops are also shown. (a) The AA sequence of fulditoxin was subjected to Protein BLAST® search for sequence homology with protein databases. The top 16 protein sequences that shared the highest sequence homology with fulditoxin are shown. Identical AA residues across all 17 sequences are shaded in grey. The AA residues that contribute to hydrogen bond formation (shaded in black) and hydrophobic interactions (underlined) in the dimeric interface of fulditoxin are highlighted across the sequences. (b) The sequence of fulditoxin as compared with the sequences of other 3FTxs, each representing a different subfamily: erabutoxin‐a, short‐chain α‐neurotoxin; α‐bungarotoxin, long‐chain α‐neurotoxin; κ‐bungarotoxin, κ‐neurotoxins; candoxin, elapid non‐conventional three‐finger α‐neurotoxin; denmotoxin, colubrid non‐conventional three‐finger α‐neurotoxins; MT2, muscarinic three‐finger toxin; cytotoxin 4, cardiotoxin; mambin, antagonist of cell‐adhesion processes; Toxin FS‐2, L‐type calcium channel antagonist; and fasciculin‐1, AChE inhibitor. (c) Comparison of the AA sequence of fulditoxin with the sequences of short‐chain 3F‐αNTxs. The conserved AA residues in short‐chain 3F‐αNTxs deemed critical for the recognition and binding to muscle‐type nAChRs are highlighted in black. (d) Comparison of the AA sequence of fulditoxin with the sequences of dimeric 3F‐NTxs. The AA residues in fulditoxin contributing to dimerization are highlighted in black; and His29 involved in Zn2+ binding is italicized and underlined. The cysteine residues involved in the formation of intermolecular disulfide linkages in the α‐cobratoxin dimer and irditoxin A–irditoxin B dimer are underlined. (e) Comparison of the AA sequence of fulditoxin with the sequences of reversible neurotoxins
