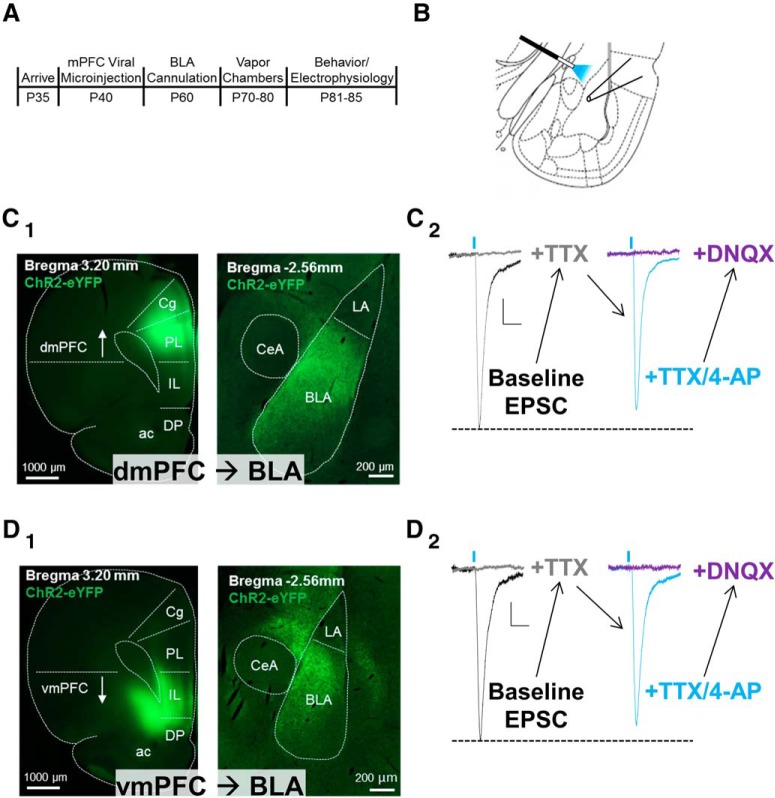
Figure 1.
The dorsal and ventral subdivisions of the mPFC make dense, monosynaptic glutamatergic synaptic connections with BLA principal neurons. A, Experimental timeline with procedures on the top and approximate age of the rats in postnatal days on the bottom. B, Schematic depicting the typical placement of the optical “stimulator” and patch electrode for electrophysiology recordings. The optical fiber delivering 470 nm blue light was placed just medial of the BLA above the stria terminalis to activate the channelrhodopsin-expressing mPFC inputs. BLA principal neurons were patched along the dorsomedial aspect of the subdivision where the YFP-expressing terminals were most dense. C1, D1, Representative fluorescent images of the mPFC injection site (left) and the resulting terminals in the BLA (right) 4 weeks after the injection of channelrhodopsin into the dmPFC (C1) or vmPFC (D1), respectively. C2, D2, Representative traces of light-evoked oEPSCs recorded from dmPFC–BLA (C2) or vmPFC–BLA (D2) synapses, respectively, in the presence of various agents. See text for details. Calibration: 20 ms, 20 pA. Blue vertical dashes represent the approximate onset of optogenetic stimulation (5 ms duration). ac, Anterior commissure; LA, lateral amygdala.