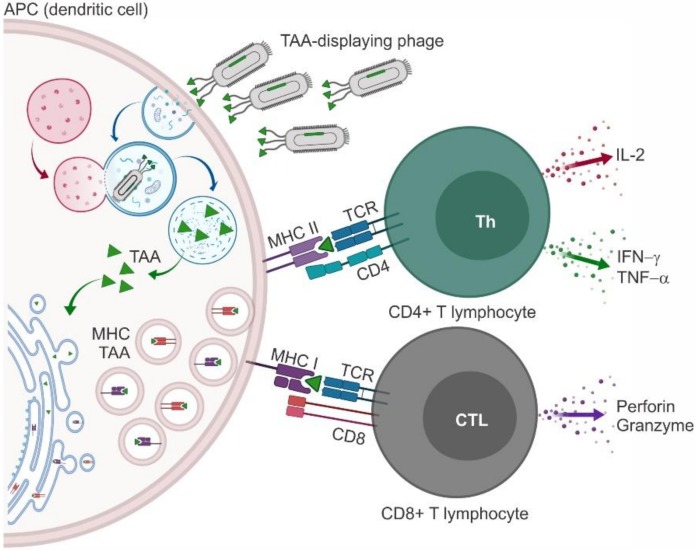
Figure 2.
Cellular response: APCs and T-lymphocytes. TAA-displaying phages are processed inside an APC via the endosome-lysosome pathway. The TAA is exposed on the APC surface complexed with MHC molecules. Naïve T lymphocytes carrying a TAA-specific TCR are activated by interaction with the TAA-MHC complex: binding to MHC class II leads to activation of CD4+ T lymphocytes and differentiation in Th cells, while binding to MHC class I leads to activation of CD8+ T lymphocytes and differentiation in CTLs. Both types of effector T cells release chemokines and cytokines to mount an immune response against the TAA. Abbreviations: APC, antigen-presenting cell; TAA, tumor-associated antigen; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; TCR, T-cell receptor; Th, T helper; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; IL-2, interleukin 2; IFN-γ, interferon γ; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α.