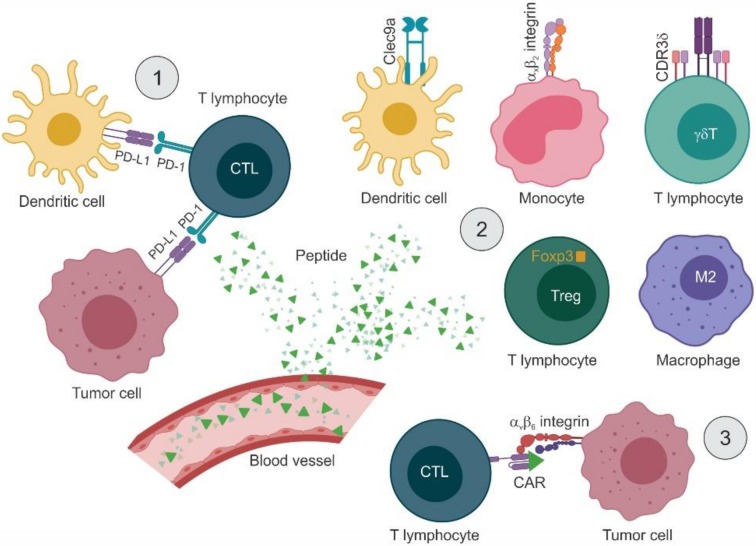
Figure 3.
Phage display-derived peptides as nanomodulators of the immune response. Peptides administered intravenously can exit the blood vessels and reach different cell types to (1) inhibit PD-1/PD-L1 interaction or (2) target immune cells for either activation (dendritic cells, monocytes, λδT lymphocytes) or inhibition (Tregs, M2-like macrophages) of their functions. (3) Selected peptides can also be exploited in a CAR strategy. Abbreviations: PD-1, programmed cell death 1; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand 1; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocytes; CDR, complementary determining region; Tregs, T regulatory cells; CAR, Chimeric Antigen Receptor.