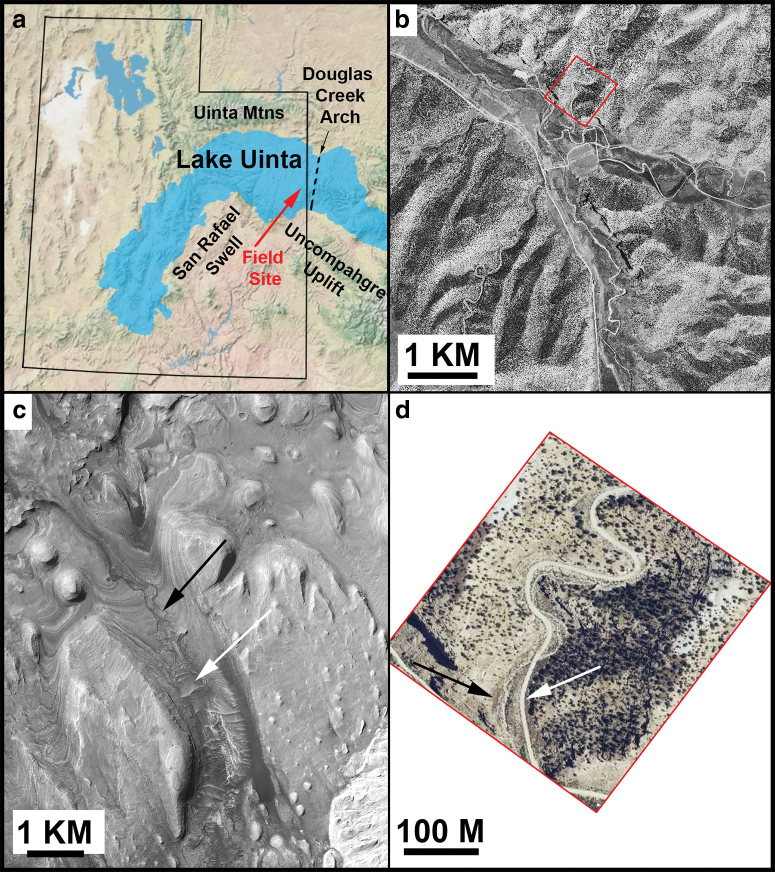
FIG. 1.
(a) Paleogeological map of Utah during the Eocene, showing the approximate boundary of Lake Uinta marked; red arrow indicates the field site. (b) Orthorectified panchromatic 1 m/pixel image from Utah Geological Survey showing context of field site; field site is in red box. (c) Gediz Vallis, Mars; white arrow indicates valley floor, at higher elevation, whereas black arrow indicates incised channel (HiRISE image PSP_009294_1750 with the subscene centered near 4.796 S, 137.413 E). (d) Area in red box in (b); black arrow indicates a wash, white arrow indicates a road at higher elevation. Both Gray Huts canyon and Gediz Vallis are characterized by gently dipping layered sedimentary rocks (USDA Farm Service Agency National Agriculture Imagery Program aerial survey image, 1 m/pixel). North is up in all images. HiRISE, High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment. Color images are available online.