Figure 5. Ca2+ influx activates ASK1 in platelets.
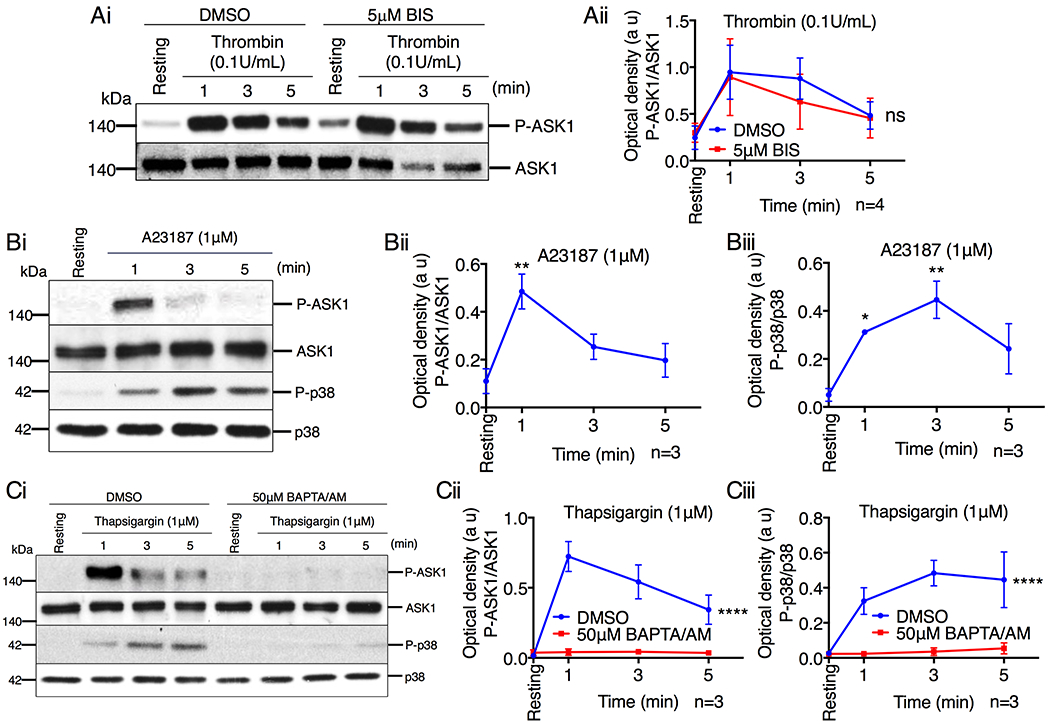
(A) Western blot analysis of human platelets pretreated with either DMSO or BIS (5μM), and stimulated with thrombin (0.1U/mL). (Ai) Images of representative immunoblots of phosphorylation of ASK1 using phospho-specific antibodies. Blots were reprobed with anti-ASK1 antibodies to ensure equal protein loading. (Aii) Quantification of the band intensity of P-ASK1 from (Ai); Not significant (ns), two-way ANOVA. (B) Representative western blot images of human platelets stimulated with A23187 (1μM). (Bi) Images of representative immunoblots of phosphorylation of ASK1 and p38 using phospho-specific antibodies. Blots were reprobed with anti-ASK1 and anti-p38 antibodies to ensure equal protein loading. Quantification of the band intensity of (Bii) P-ASK1 and (Biii) P-p38 from (Bi), *P<0.05, **P<0.01, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. (C) Western blot analysis of human platelets pretreated with either DMSO or BAPTA/AM (50μM) and stimulated with thapsigargin (1μM). (Ci) Images of representative immunoblots of phosphorylation of ASK1 and p38 using phospho-specific antibodies. Blots were reprobed with anti-ASK1 and anti-p38 antibodies to ensure equal protein loading. Quantification of the band intensity of (Cii) P-ASK1 and (Ciii) P-p38 from (Ci), ****P<0.0001, two-way ANOVA.
