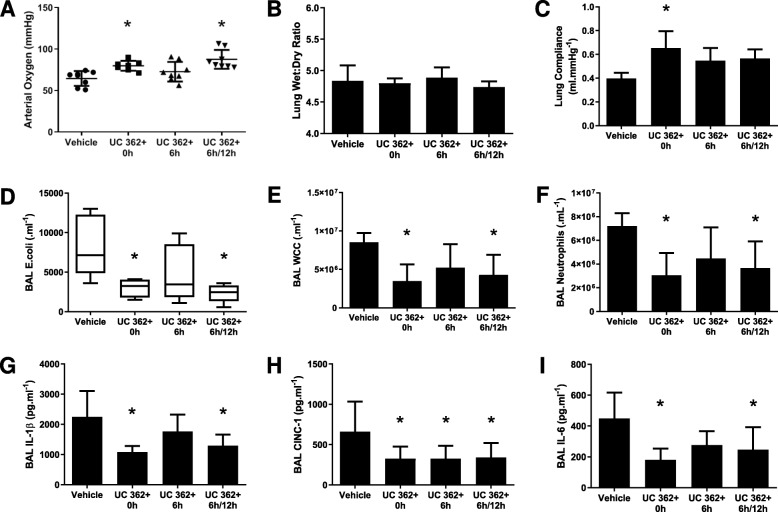
Fig. 5.
Repeat dosing with CD362+ UC-hMSCs extends the therapeutic window in E. coli-induced ARDS. CD362+ UC-hMSCs administered contemporaneously or at 6 h plus 12 h post-commencement of E. coli ARDS, ameliorated the decrement in arterial oxygenation (a), reduced lung E. coli bacterial load (d), total BAL infiltrating leukocytes (e) and neutrophils (f) compared to vehicle control or a single dose of CD362+ UC-hMSCs delivered 6 h post-induction. There were no significant changes in lung tissue wet to dry ratio (b), and the contemporaneous delivery alone significantly reversed the decrease in lung static compliance (c). CD362+ UC-hMSCs administered contemporaneously or at 6 h plus 12 h post-E. coli injury significantly reduced E. coli ARDS-induced levels of BAL inflammatory cytokines IL-1β (h), and BAL IL-6 (j), while each dosing regimen decreased BAL CINC-1 (i). Abbreviations: vehicle, treatment with vehicle alone; UC 362+, umbilical cord-derived CD362+ hMSC; 0 h, delivery at 0 h post-E. coli instillation alone; 6 h, delivered at 6 h post-E. coli instillation alone; 6 h + 12 h, delivered at 6 h and 12 h post-E. coli instillation; BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; IL-1β, interleukin 1 beta; CINC-1, cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant 1; IL-6, interleukin 6. Error bars represent standard deviation. *Significantly (P < 0.05) different from the vehicle control group