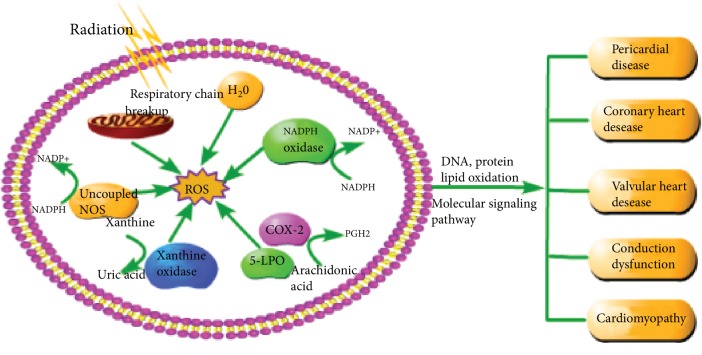
Figure 1.
Formation of ROS after radiation and the general manifestation of cardiotoxicity. As described in the article, the sources of ROS are varied, even under the radiation conditions. IR can directly cause the respiratory chain of mitochondria to breakup and cause the decomposition of water molecules, leading to respiratory chain dysfunction and ROS production, reducing antioxidant capacity. NADPH oxidase is a family of multisubunit complex enzymes that catalyze the conversion of oxygen into O2− by using NADPH as an electron source, which is present in vascular endothelia cells, smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, and cardiomyocytes. The mechanism of uncoupled NOSs is similar to NADPH oxidase. Xanthine oxidase catalyzes the conversion of xanthine to uric acid while H2O2 and O2− are generated at the same time. In addition, COX-2 and 5-LPO produce PGH2 accompanied by ROS formation during catalytic arachidonic acid metabolism. ROS can interact with macrobiomolecules (DNA, protein, and lipid), causing oxidation of DNA, proteins, and lipids and cause cardiac damage through some signaling pathways, which are described in article above. The cardiac damage includes pericardial disease, coronary heart disease, heart valve disease, conduction disorders, and cardiomyopathy.