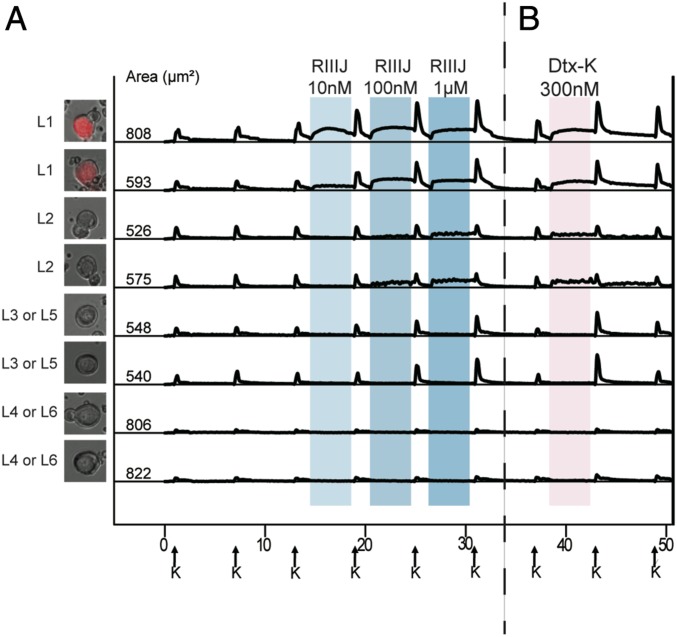
Fig. 2.
(A) L1 neurons are proprioceptors. (B) Dtx-K elicits effects similar to RIIIJ. (A) Genetically labeled proprioceptor neurons were identified as L1 neurons by their responses to RIIIJ as observed by calcium imaging. The L1 response phenotype to RIIIJ was exclusively observed in the labeled proprioceptive neurons. L2 to L6 neurons were not proprioceptors as indicated by calcium imaging. Thus, RIIIJ can be reliably used to identify proprioceptive neurons in dissociated culture of mouse DRG neurons. We used PV-IRES-Cre-ER driver mice crossed with Ai14 reporter mice to drive the expression of tdTomato (red) in proprioceptive neurons of the progeny. Left shows the bright-field image overlaid with the tdTomato image of the proprioceptor neuron from which the data were acquired. (B) Dtx-K elicits effects similar to RIIIJ. In each subclass, the phenotypic calcium response to the application of Dtx-K was similar to the effects elicited by the application of different concentrations of RIIIJ. However, the effects of Dtx-K were often slowly reversible compared with RIIIJ. The column of cell images (Left) shows the bright-field image overlaid with the GFP fluorescence of the neuron from which the data are acquired. Numbers indicate the cross-sectional area of each cell soma in micrometers2. On the x axis (time in minutes), arrows indicate 15-s applications of 20 mM K+ at 7-min intervals. Shaded areas indicate the presence of different concentrations of RIIIJ or Dtx-K. On the y axis, the ratio of 340/380 nM as a measure of relative intracellular calcium levels is normalized to a scale of zero to one.