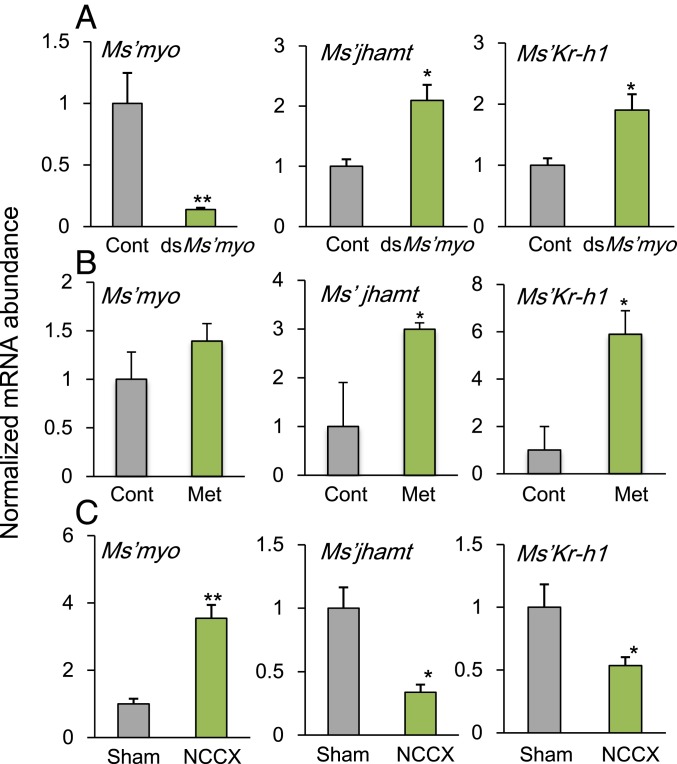
Fig. 3.
Effects of dsMs’myo (A), methoprene treatments (B), or NCC I+II severance (C) on the relative abundance of Ms’myo, Ms’jhamt, and Ms’Kr-h1 mRNAs in the head of Modicogryllus siamensis. Values are an average of four samples containing three heads each, shown relative to those of the DsRed2RNAi controls (A and B) or those of sham operated crickets (C). Males and females were pooled. The abundance of Ms’rp49 mRNA was used as an internal reference. Error bars indicate SEM. Asterisks represent significant differences between control and treated crickets: **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, t test. (A) mRNA levels were measured on day 1 in the sixth instar nymphs treated with dsDsRed2 (black) or dsMs’myo (light green) on day 1 in the fourth instar under LD (16L:8D) at 30 °C. The samples were collected at 6 h after light-on (ZT6). Ms’myonRNAi significantly suppressed Ms’myo mRNA levels, whereas Ms’jhamt and Ms’Kr-h1 levels were significantly up-regulated. (B) mRNA levels were measured on day 3 in the sixth instar nymphs, which were treated with methoprene on day 3 of the fifth instar. Methoprene up-regulates Ms’jhamt and Ms’Kr-h1 expression but had no clear effect on Ms’myo levels. (C) mRNA levels were measured 24 h after the NCC I+II severance (NCCX) on day 1 of the seventh instar nymphs. The operation resulted in the up-regulation of Ms’myo and down-regulation of Ms’jhamt and Ms’Kr-h1. For further explanations, see text.