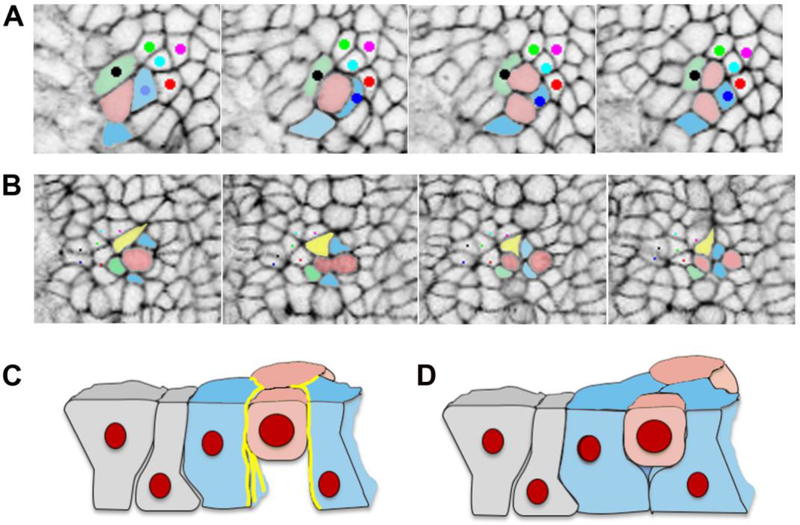
Figure 4. Cell division generating cell rearrangement in the mouse neural plate.
A. In this example, the pink cell divides, and the daughter cells stay in contact, while one pink daughter cell separates the blue and green cells. B. In this example the pink cell divides, and the two blue cells insert themselves between the two pink daughter cells, and one pink daughter cell separates the yellow and green cells. C and D. Schematics of the behavior of the basal ends of neighboring cells during cell division, based on published data for chick epiblast [115]. C. When actin and myosin localization (yellow lines) is strong and cadherin low at the lateral boundaries of cells neighboring a mitotic cell, these cells do not fill in the space basal to the mitotic cell to form new intercellular junctions, and as a result do not separate the daughter cells. D. When actin and myosin are not strongly localized at the lateral boundaries of cells neighboring a mitotic cell, these cells are able to fill in the space basal to the mitotic cell, forming new junctions and separating the daughter cells.