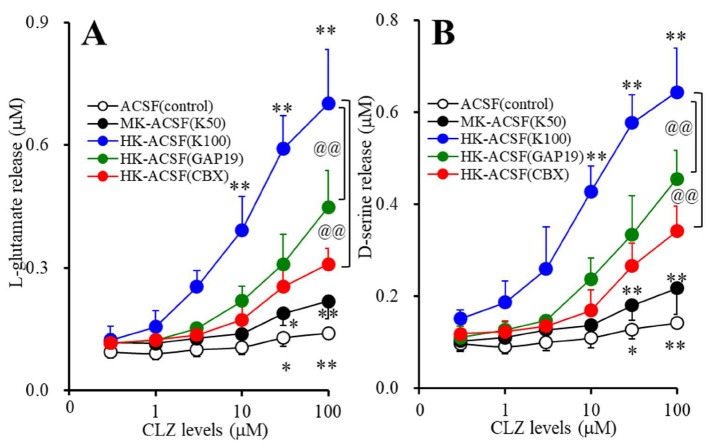
Figure 2.
Concentration-dependent effects of subchronic administration of CLZ on basal and K+-evoked astroglial releases of L-glutamate (A) and D-serine (B). Astrocytes were incubated in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium containing 10% fetal calf serum (fDMEM) containing CLZ (0, 1, 3, 10, 30, or 100 μM) for 7 days. After wash-out, astrocytes were incubated in 100 μL ACSF containing the same concentration of CLZ for 60 min (pretreatment incubation). After pretreatment incubation, to determine the K+-evoked astroglial releases of L-glutamate and D-serine, astrocytes were incubated in ACSF (3.0 mM K+: opened circles), MK-ACSF (50.0 mM K+: closed circles), or HK-ACSF (100.0 mM K+: blue circles) containing the same concentration of CLZ during pretreatment incubation for 20 min. To clarify the astroglial releases of L-glutamate and D-serine associated with Cxs, astrocytes were incubated in HK-ACSF containing GAP19 (20 μM) (green circles) or CBX (100 μM) (red circles) with the same concentration of CLZ during pretreatment incubation for 20 min, and then incubate medium (ACSF, MK-ACSF, or HK-ACSF) was collected for analysis. Ordinate: mean ± SD (n = 6) of extracellular levels of l-glutamate and d-serine (μM). Abscissa: concentration of CLZ (μM). * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. CLZ free by MANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. @@ p < 0.01 vs. HK-ACSF by MANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.