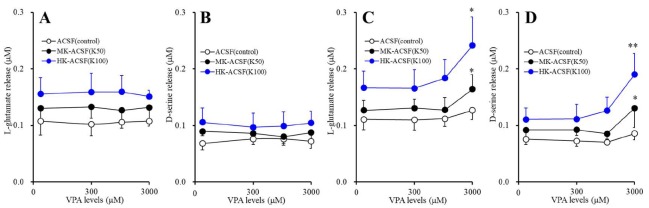
Figure 3.
Concentration-dependent effects of acute administration of VPA (valproate) on basal and K+-evoked astroglial releases of l-glutamate (A) and d-serine (B). After wash-out, astrocytes were incubated in ACSF containing VPA (0, 300, 1000, or 3000 μM) for 60 min (pretreatment incubation). After pretreatment incubation, to determine the K+-evoked astroglial releases of L-glutamate and d-serine, astrocytes were incubated in ACSF (3.0 mM K+: opened circles), MK-ACSF (50.0 mM K+: closed circles), or HK-ACSF (100.0 mM K+: blue circles) containing the same concentration of VPA during pretreatment incubation for 20 min. Concentration-dependent effects of subchronic administration of VPA on basal and K+-evoked astroglial releases of l-glutamate (C) and d-serine (D). Astrocytes were incubated in fDMEM containing VPA (0, 300, 1000, or 3000 μM) for 7 days. After wash-out, astrocytes were incubated in ACSF containing the same concentration of VPA (pretreatment incubation). After pretreatment, to clarify the K+-evoked astroglial releases of l-glutamate and d-serine, astrocytes were incubated in ACSF (opened circles), MK-ACSF (closed circles), or HK-ACSF (blue circles) containing the same concentration of VPA during pretreatment incubation for 20 min, and then incubate medium (ACSF, MK-ACSF, or HK-ACSF) was collected for analysis. Ordinate: mean ± SD (n = 6) of extracellular levels of l-glutamate and d-serine (μM). Abscissa: concentration of VPA (μM). * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. VPA free by MANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.