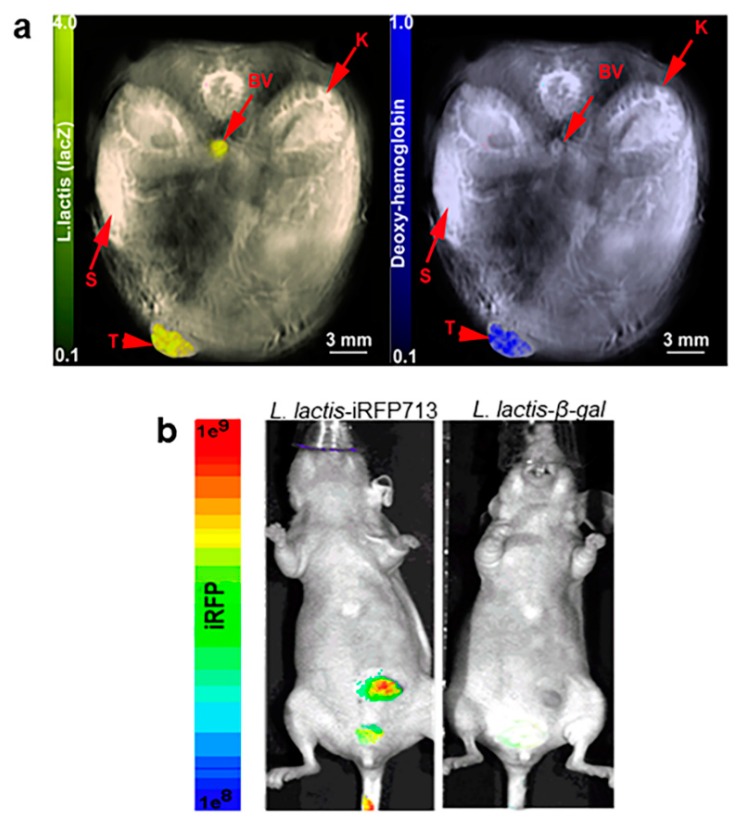
Figure 6.
Feasibility of L. lactis-β-gal to establish within areas of tumor hypoxia using MSOT or near infrared imaging: (a) L. lactis-β-gal (1.5 × 109 CFU/50 µL) was i.v. injected into mice and detected within tumor. Mice were anesthetized using 0.1 L O2 and 0.9 L medical air with 1.5% isoflurane for imaging following 24 h post-injection using MSOT. Mouse images were reconstructed and multispectrally processed using standard techniques. (Left) L. lactis-β-gal was demonstrated within the hypoxic regions of the tumor as depicted by deoxy-hemoglobin (Right). Organs are indicated using arrows: blood vessel (BV); kidney (K); spleen (S); tumor (T). (b) Feasibility of detection of L. lactis-IRFP713 using NIR fluorescence imaging. Mice i.v. injected with L. lactis-IRFP713 had identifiable signals (left), whereas the blue color-LacZ does not demonstrate fluorescent signals (right). A representative MSOT or NIR images at 24 h post-intravenous injection of L. lactis is shown from three preformed.