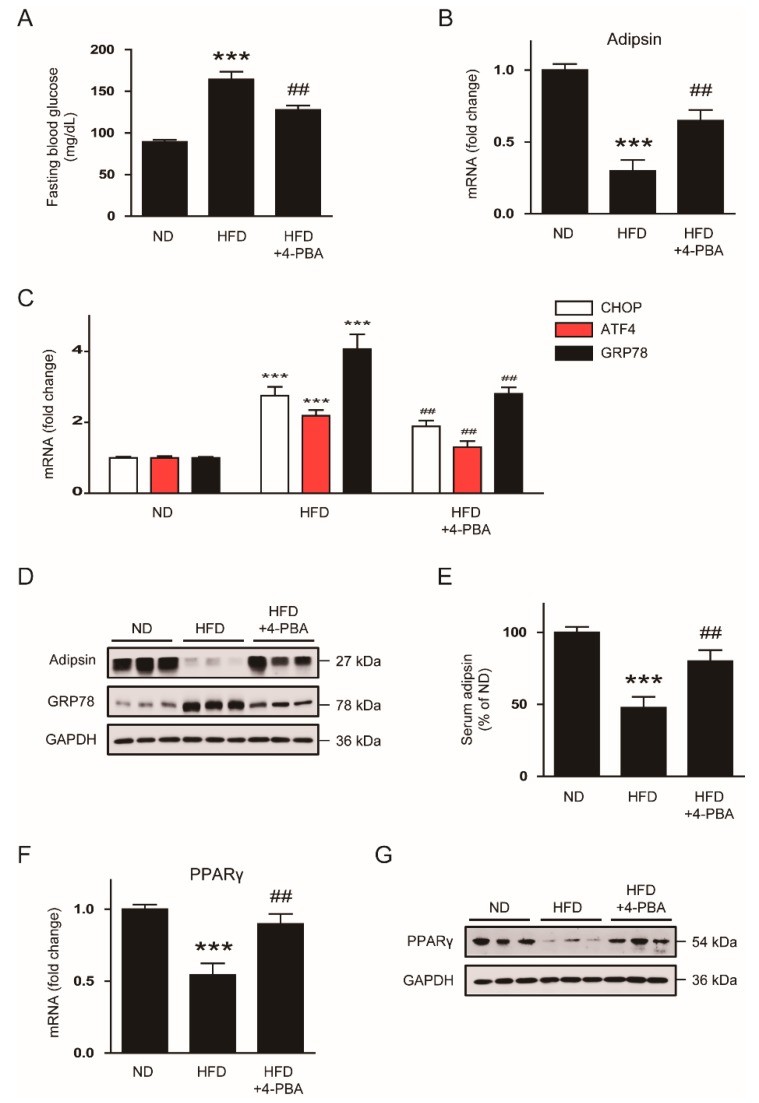
Figure 7.
Administration of 4-PBA reverses the ER stress-mediated downregulation of adipsin in vivo. C57BL/6N mice were divided into two groups fed either a normal chow diet (ND; n = 8) or a high-fat diet (HFD; n = 16). After 8 weeks, the HFD-fed mice were divided into two sub-groups: an HFD group (n = 8); an HFD plus 4-PBA group (HFD + 4-PBA; n = 8). The HFD group and the HFD + 4-PBA group were fed with an HFD and intraperitoneally administered with vehicle (phosphate-buffered saline) or 4-PBA (1 g/kg per day) once daily for an additional 4 weeks, respectively. The ND group continued to receive an ND throughout the entire experimental period. After 4 weeks of treatment, all mice were sacrificed. (A) Fasting blood glucose levels. (B) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of adipsin in gWATs. (C) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of CHOP, ATF4, and GRP78 in gWATs. (D) Western blot analysis of adipsin, GRP78, and GAPDH in gWATs. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Each lane represents an individual animal. (E) Serum levels of circulating adipsin. (F) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of PPARγ in gWATs. (G) Western blot analysis of PPARγ and GAPDH in gWATs. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Each lane represents an individual animal. All data are represented as the mean ± SEM. *** p < 0.001 vs. ND-fed mice. ## p < 0.01 vs. HFD-fed mice.