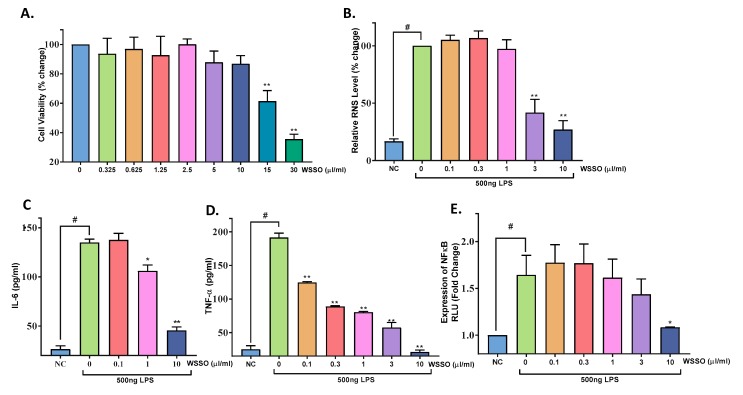
Figure 9.
WSSO reduced total RNS in RAW264.7 cells and inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines secretion by modulating the NFκB pathway in THP-1 cells: (A) Effect of WSSO on THP-1 cell viability was determined by MTT assay; loss in cell viability was observed at 15 μL/mL and above concentrations. (B) Reactive nitrogen species was measured in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells after treatment with non-toxic concentrations of WSSO. A significant reduction (p < 0.001) in RNS level (~80%) was observed at 10 μL/mL. LPS induced upregulation of cytokine IL-6 (C) and TNF-α (D) in THP-1 cells, and was inhibited by treatment with WSSO. Highly significant (p < 0.0001) inhibition of TNF-α was observed at all the WSSO concentrations tested, whereas significant inhibition in IL-6 expression was observed at concentrations of 1–10 μL/mL. NFκB promoter luciferase reporter assay (E) was performed in THP-1. Concentration-dependent inhibition of NFκB activity by WSSO was significant (p < 0.01) at 10 μL/mL. Values are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent experiments, p-values # p < 0.001 (LPS-alone vs. non-treated cells); * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.0001 (LPS alone vs. LPS + WSSO-treated cells).