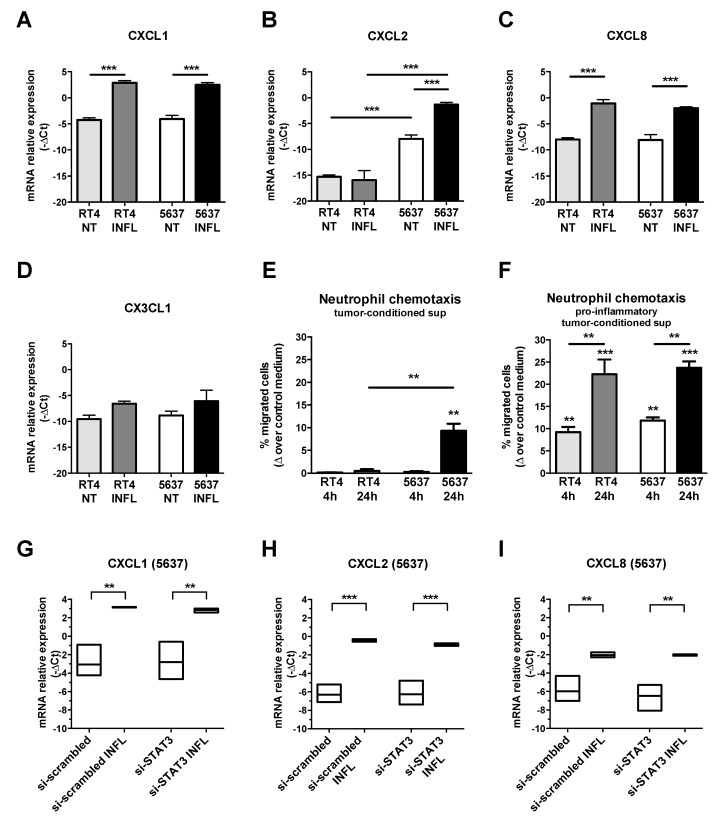
Figure 10.
Modulation of TAN-attracting CK in UBC cell line. Column bars (A–D) showing the mean ± SD of CKs mRNA relative gene expression (-ΔCt, n = 3), measured by qRT-PCR in luminal-type RT4 and basal-type 5637 UBC cell lines. After stimulation with a cocktail of proinflammatory cytokines, a significant induction of the CXCL1 and CXCL8 mRNA (A,C) is observed in both UBC cell lines. CXCL2 is significantly enriched in basal-type 5637 UBC cell line compared to luminal-type RT4 cells both at resting and after stimulation (B). Column bars (E,F) showing neutrophil chemotaxis towards tumor-conditioned supernatants from luminal-type RT4 or basal-type 5637 UBC cell lines untreated (E) or stimulated for 4 or 24 h with a pro-inflammatory cytokine cocktail (F) (n = 3). Chemotaxis is reported as increased percentage of migrated cells (expressed as % of total cell input, mean ± SD) induced by tumor-conditioned supernatants over the control medium. Floating bars (G–I) showing that CKs’ mRNA is not modulated by siRNA STAT3 in 5637 cell line stimulated with pro-inflammatory cytokine cocktail (mean, range; n = 3). A one-way ANOVA test was used for all statistical analysis and pairwise comparisons p values were adjusted for multiple comparisons; significant results were showed (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001). INFL, with the pro-inflammatory cytokine cocktail (TNF-a, IL6, IL1b); supernatants, sup.