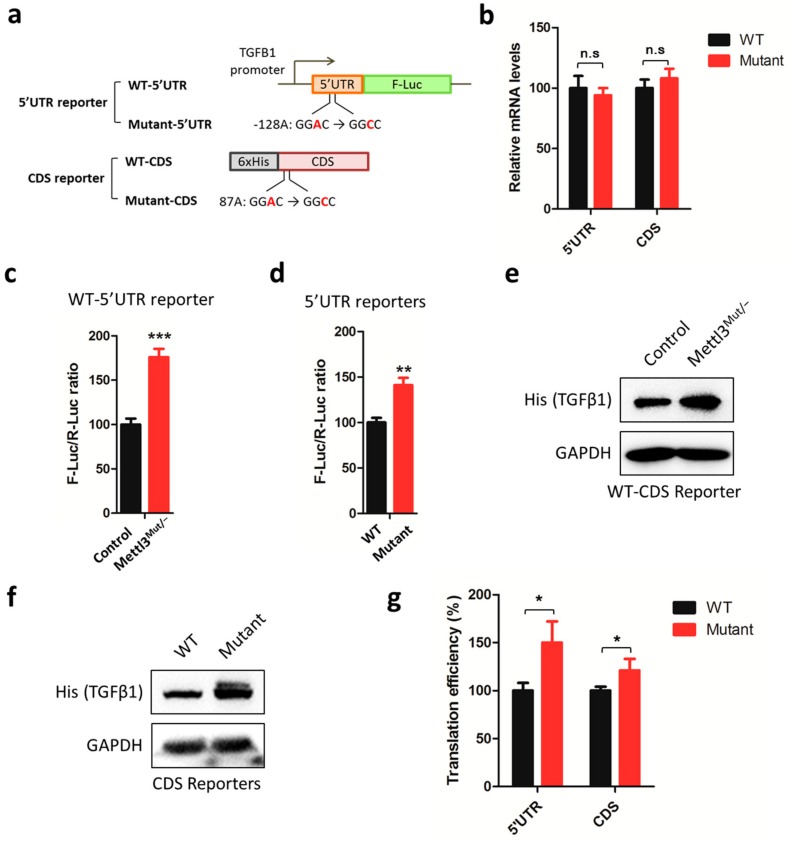
Figure 4.
m6A methylation on both the 5′UTR and CDS regions of TGFB1 mRNA controls its translation efficiency. (a) Reporters for 5′UTR and CDS regions of TGFB1 mRNA. Potential m6A sites were mutated (GGAC to GGCC); (b) wild type (WT) and mutated reporters were transfected in HeLa cells for 48 h. Expression levels of reporter mRNA were measured by qRT-PCR: FLUC mRNA for 5′UTR reporter, normalized to RLUC mRNA levels; TGFB1 mRNA for the CDS reporter, normalized to GAPDH mRNA levels; (c) the WT-5′UTR reporter was co-transfected with TK-Rluc reporter in control and Mettl3Mut/− HeLa cells for 48 h. Dual-luciferase assay was performed to measure F-Luc production, which was normalized to R-Luc levels; (d) WT-5′UTR or Mutant-5′UTR reporter were co-transfected with TK-Rluc reporter in HeLa cells for 48 h. Dual-luciferase assay was performed to measure F-Luc production, which was normalized to R-Luc levels; (e) WT-CDS reporter was transfected in control and Mettl3Mut/− HeLa cells for 48 h. Expression levels of exogenous TGFβ1 (His) were measured by Western blot; (f) WT-CDS or Mutant-CDS reporter were transfected in HeLa cells for 48 h. Expression levels of exogenous TGFβ1 (His) were measured by Western blot; (g) Translation efficiency of WT and TGFβ1 mutant is defined as the quotient of reporter protein production divided by mRNA abundance [11]. For 5′UTR, reporter protein production was determined from dual-luciferase assay; for CDS, reporter protein production was analyzed by ImageJ from Western blot. Data are presented as means ± SD from three independent experiments. Student’s t-test, n.s, no significant; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 compared with control.