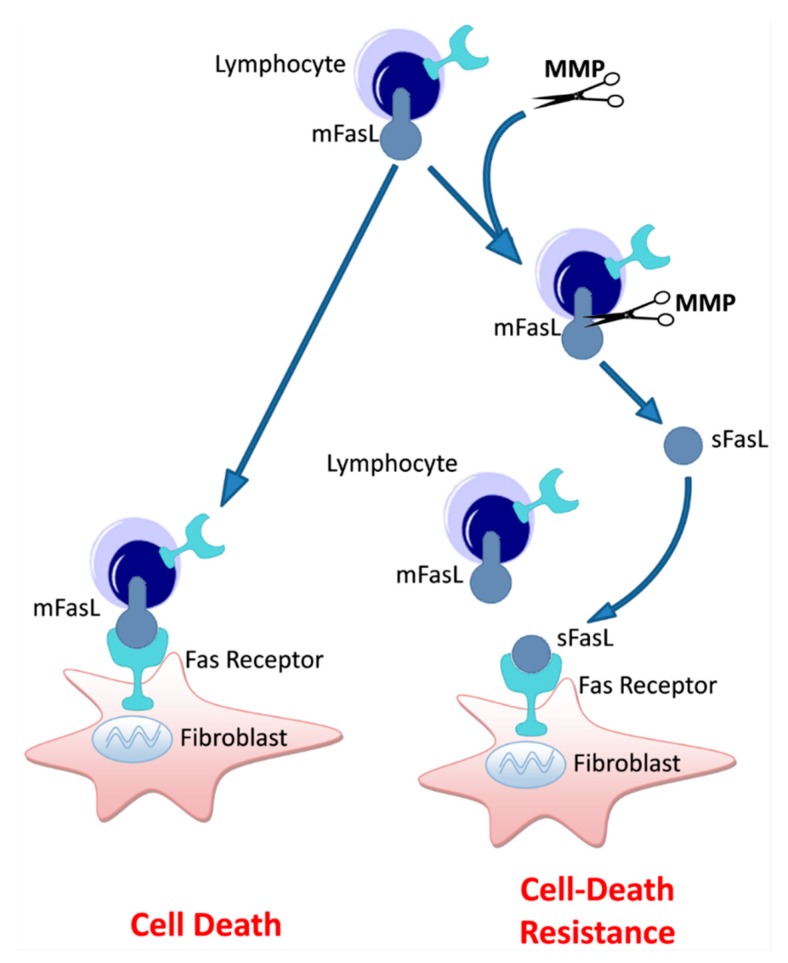
Figure 5.
Simplified scheme of the proposed model of sFasL, MMP-mediated, immune cell-induced myofibroblast death regulation during lung fibrosis. Lymphocytes are known to express mFasL that enables T cell-induced myofibroblast cell death with resolution of fibrosis. In fibrotic-lung myofibroblasts, in the presence of MMPs, high levels of sFasL are detected due to mFasL cleavage. High sFasL in the milieu competes with mFasL and limits T cell-induced cell death. sFasL secreted by fibrotic lung fibroblasts is an additional mechanism of their resistance to cell death and their uninterrupted accumulation in lung fibrosis.