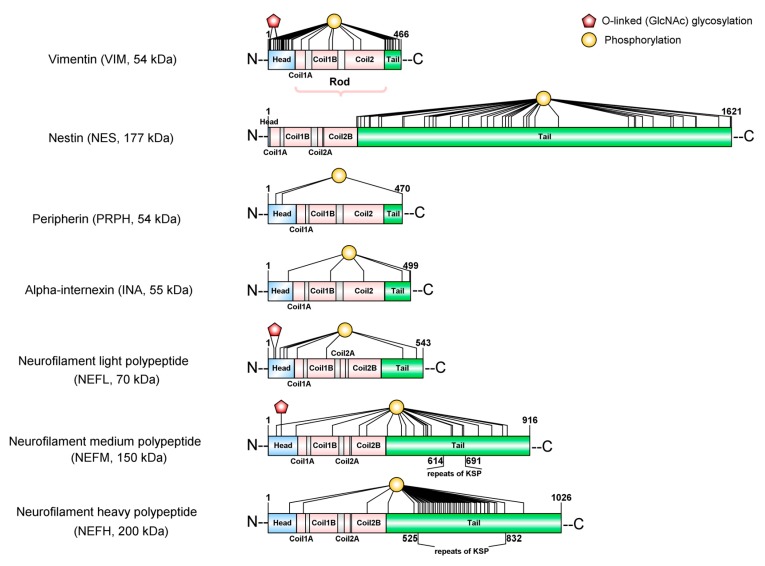
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the domains and posttranslational modifications of intermediate filaments. Vimentin and nestin are the subunits of neurofilaments (NFs) in the developing nervous system. Neurofilament light (NF-L), neurofilament middle (NF-M), neurofilament heavy (NF-H), α-internexin, and peripherin are subunits of NFs in the mature nervous system. All subunits share a conserved molecular structure composed by (i) an alpha-helical coiled-coil rod domain; (ii) a variable globular head at the N-terminal; (iii) and C-terminal tail domains. The chemical properties neurofilament subunits are modulated mostly by two posttranslational modifications: phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation. The tail domains of NF-M and NF-H are subject to extensive phosphorylation on Lysine-Serine-Proline repeats (KSP). NF proteins (NF-L, NF-M, NF-H) and vimentin are glycosylated by O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) at the hydroxyl groups of serine (Ser) or threonine (Thr) residues of their head domains. Phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation residues are shown.