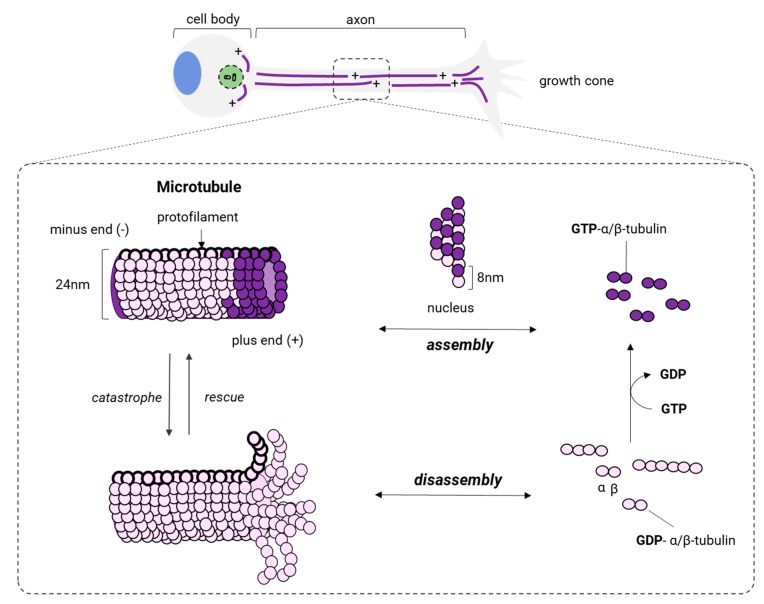
Figure 7.
Microtubules assembly. In neurons, microtubules are assembled from the centrosome, which is located in the neuronal soma, and then they are released to be transported towards a mature axon or the growth cone of a growing neurite. On the one hand, microtubules in an axon have different sizes, but they have the same polarity; on the other hand, the microtubules in dendrites have a mixed polarity. While microtubules are transported through an axon, they suffer several cycles of growth and shortening in a process known as microtubule assembly dynamics. This process is summarized in the center of the image. The dimers of α/β-tubulin bound to GTP of the protofilament provoke the growth of the microtubule, whereas the dimers of α/β-tubulin bound to GDP of the protofilament favors disassembly. Microtubule binding proteins regulate the exchange rate between growth (rescue) and shortening (catastrophe).