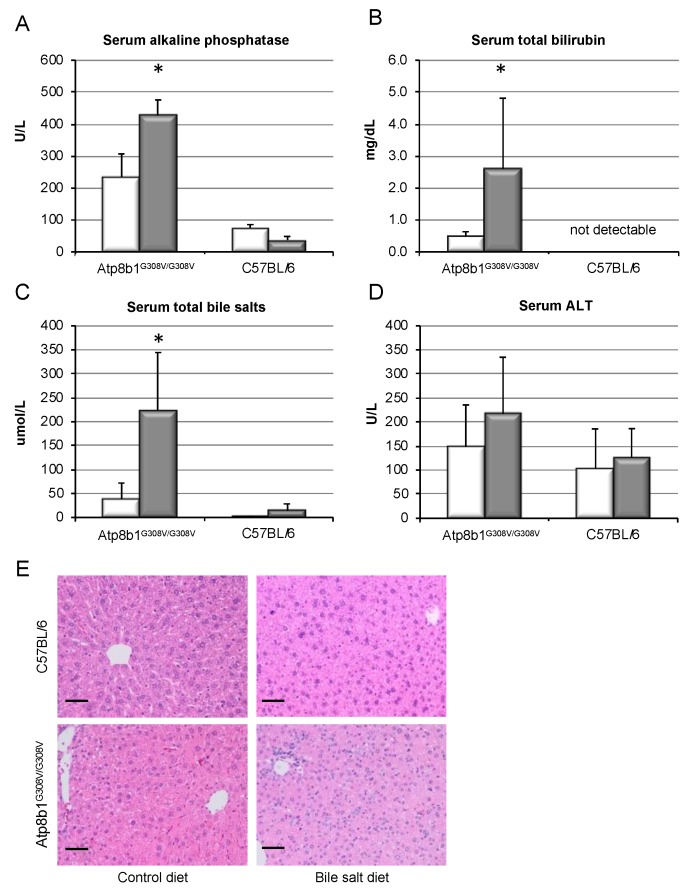
Figure 1.
Bile salt feeding induces chronic cholestasis in Atp8b1G308V/G308V mice. 8 week old Atp8b1G308V/G308V and wild-type mice (C57BL/6) were fed a standard diet (white bars) or a cholate- (CA, 0.1% w/w) and glycochenodeoxycholate (GCDCA, 0.3% w/w)-enriched diet (grey bars) to induce cholestasis and a humanized bile salt pool for 8 weeks. Serum values for alkaline phosphatase (A), total bilirubin (B), total bile salts (C), and ALT (D) were determined as described. Results are shown as mean ± standard deviation (n = 4 for C57BL/6 and n = 7 for Atp8b1G308V/G308V, * p < 0.05, t-test). HE stainings were evaluated for liver cell damage, necrosis, or inflammation, without major findings (E). All animals showed a non-specific heterogenicity in cell and nuclear size, but not wild-type animals on control diet. Black bar represents 50 µm.