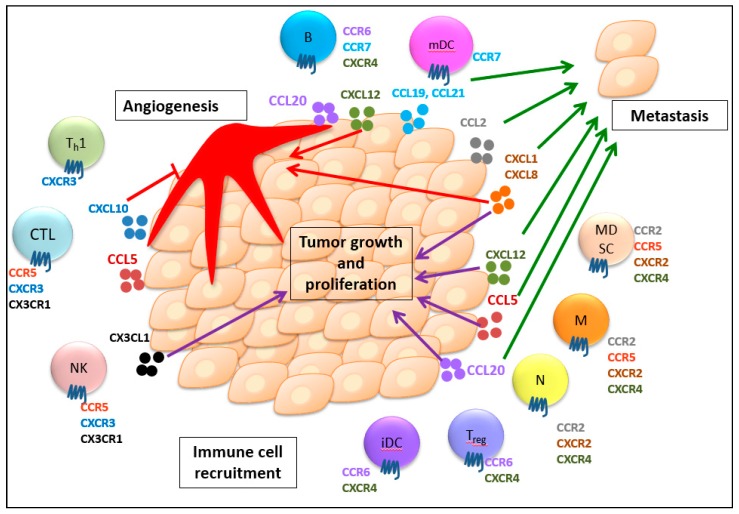
Figure 1.
Multifaceted roles of chemokines and their receptors in immune cell recruitment, tumor growth and proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Chemokines guide the trafficking of different immune cells expressing their respective receptors into the tumor microenvironment, which induces both anti- and protumor immunity. Additionally, the chemokine system generally stimulates tumor growth and proliferation. Chemokines can also regulate angiogenesis with their angiogenic or angiostatic functions. Furthermore, chemokines are involved in tumor migration to secondary sites to develop metastasis. CTL, CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte; Th1, T helper cell; NK, natural killer cell; Treg, regulatory T cell; B, B cell; iDC, immature dendritic cells; mDC, mature dendritic cell; N, neutrophil, M, macrophage; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell. The purple arrows show the promotion of tumor growth and proliferation. The red arrows indicate the angiogenic effect. The red T line indicates the angiostatic effect. The green arrows indicate the promotion of metastasis. (For detailed information, please see the text.).