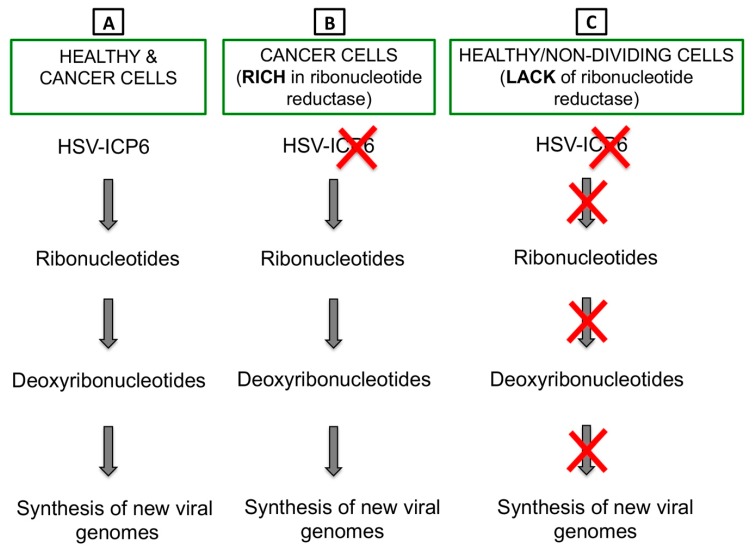
Figure 3.
ICP6 inactivation drives tumor-specific replication of OHSV-IL12. (A) ICP6 encodes for large subunit of ribonucleotide reductase, which controls nucleotide metabolism and helps HSV to replicate in normal or healthy host cells that are inherently lacking or have insufficient nucleotide pools. (B) Cancer cells are rich in ribonucleotide reductase, thus HSV with an inactivated ICP6 does not hamper DNA synthesis in cancer cells. (C) Healthy or non-dividing cells lack ribonucleotide reductase. Thus, infection of healthy cells with an ICP6-inactivated HSV leads to no nucleotide metabolism and no viral DNA replication.