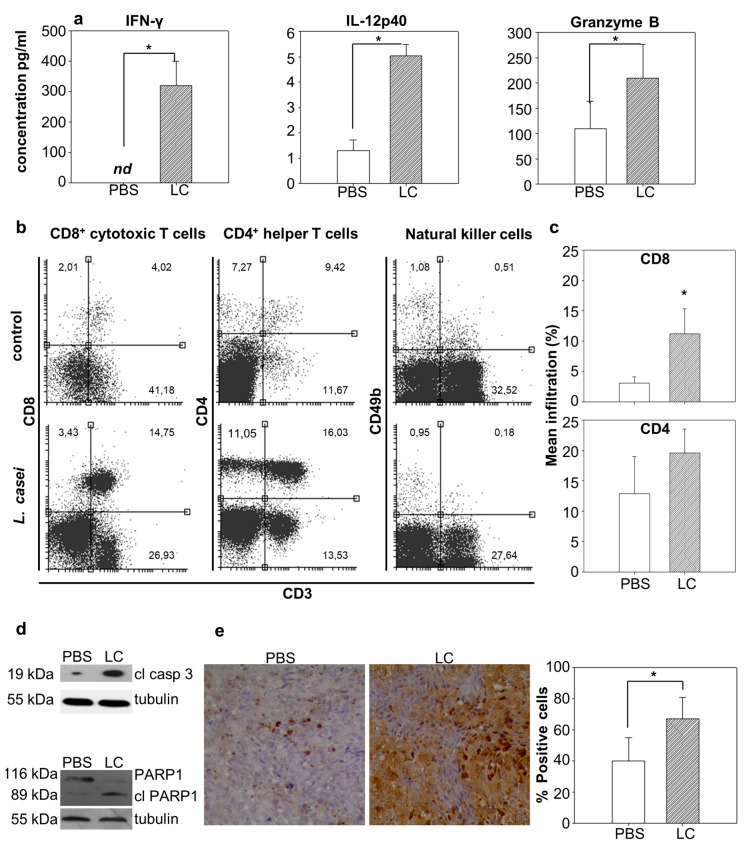
Figure 4.
Dietary oral administration of probiotic Lactobacillus casei (LC) resulted in distinct immunoadjuvant and pro-apoptotic activities in tumor-bearing mice. Excised tumors from tumor-bearing LC-treated or control (PBS-treated) mice (n = 6) were either fixed in formalin, cut in sections, stained and observed under a microscope or mechanically homogenized. Homogenized tumors were further treated for protein isolation and analysis with ELISA and western blot, or enzymatically digested for cell isolation and flow cytometry analysis. (a) Cytokine production (IFN-γ, IL-12p40, Granzyme B) in the tumor tissue excised from treated animals as compared to tumor tissue from control mice; (b) Representative dot plots showing the percentage of each subtype in TILs; (c) Diagram of the frequency of TILs as percentage of mean infiltration; (d) Western blot analysis for the cleavage of caspase 3 and PARP1. Please note the increase in cleaved caspase 3 and cleaved PARP1 in LC-treated mice as compared to PBS-treated mice; (e) Representative images of tumor sections from control and LC-treated mice, stained for cleaved caspase 3. Please note the increase in the percentage of positive cells for caspase 3 activation in sections originating from animals that received oral administration of live L. casei. *, p < 0.05, groups were repeated three times.