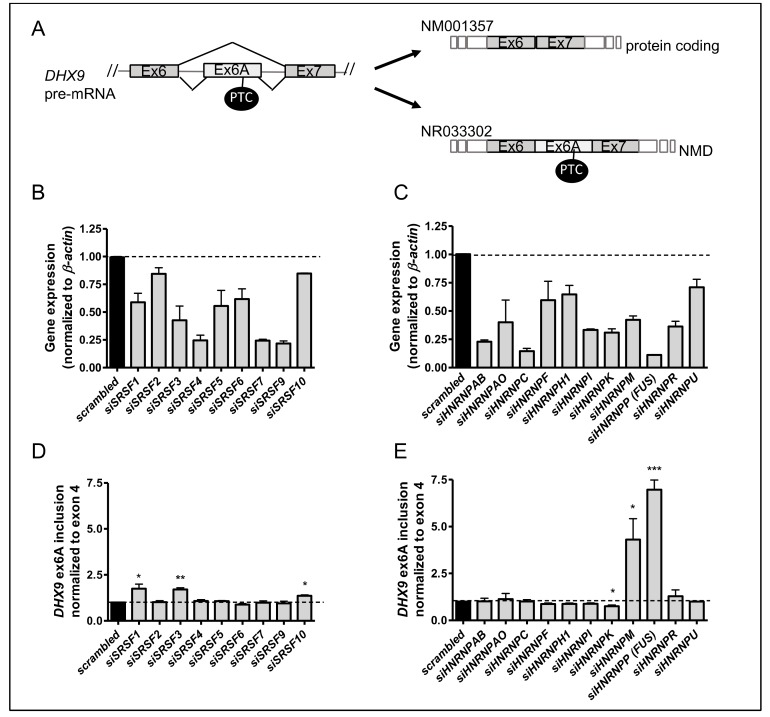
Figure 3.
Regulation of DHX9 alternative splicing. (A) Schematic representation of the alternative splicing of exon 6A in DHX9 pre-mRNA. Exclusion of the poison exon 6A in DHX9 mRNA leads to the main transcript (NM001357) encoding the full-length DHX9 protein (upper part). Exon 6A inclusion leads to the alternative noncoding transcript NR033302, containing a premature stop codon (PTC) and targeted to the NMD machinery. (B–E) Histograms represents RT-qPCR analysis of a siRNA library to downregulate the expression of SR proteins (B) (one-way ANOVA p-value < 0.0001; Bonferroni correction for siSRSF6 p-value < 0.05; siSRSF1 and siSRSF5 p-value < 0.005; siSRSF3, siSRSF4, siSRSF7, siSRSF9 p-value < 0.001, siSRSF2 and siSRSF10 p-value > 0.05) or hnRNPs (C) (ANOVA p-value < 0.0001; Bonferroni correction for sihnRNPF and sihnRNPH1 p-value < 0.05; siHNRNPAB, siHNRNPAO, siHNRNPC, siHNRNPK, siHNRNPI, siHNRNPM, siHNRNPP, and siHNRNPR p-value < 0.001, siHNRNPU p-value > 0.05). DHX9 Exon 6A (Ex6a) inclusion was monitored by RT-qPCR and normalized to the constitutive exon 4 (D,E). Reported values represent the average (± S.D.) of at least three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA, with p-value < 0.0001 (D,E) and with Bonferroni post-hoc test. (p-value: *** < 0.001, ** < 0.01, *< 0.05).