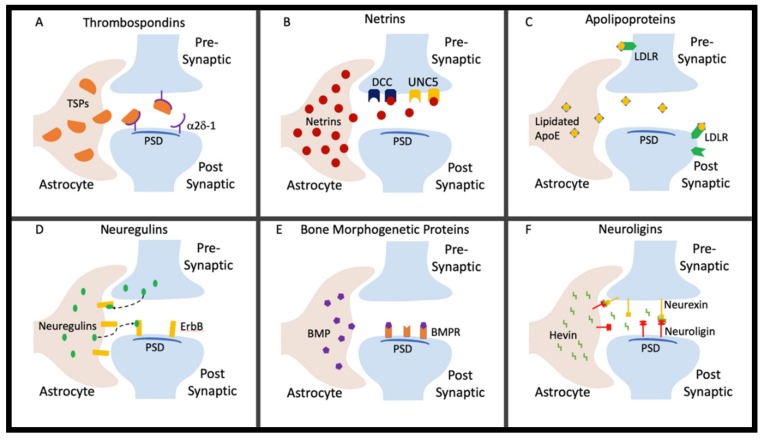
Figure 1.
Astrocytes secrete factors that regulate extracellular matrix protein signaling, formation and maintenance of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), axonal growth, homeostasis of the synaptic microenvironment, synaptogenesis, and the promotion of synaptic diversity. (A) Thrombospondins bind to the neuronal receptor α2δ-1 at the postsynaptic density to form a silent synapse. (B) Netrins bind to multiple receptors on the presynaptic terminus such as Deleted in Colorectal Cancer (DCC) and UNC-5. (C) Apolipoproteins containing cholesterol and lipids are secreted from the astrocyte and bind to the receptors on the presynaptic and postsynaptic shafts. (D) Neuregulins are secreted by the presynaptic terminus and, in higher concentrations, astrocytes. Neuregulins secreted by the presynaptic terminus bind to ErbB receptors on the astrocyte, while neuregulins secreted by astrocytes bind to ErbB receptors on the postsynaptic terminus. (E) Bone morphogenetic proteins are secreted by astrocytes and bind to bone morphogenetic protein receptors (BMPRs) at the postsynaptic density. (F) Neuroligins located postsynaptically and on astrocytes bind neurexins on the presynaptic terminus directly and indirectly. Incompatible proteins are bridged by astrocyte-secreted hevin to stabilize the synapse.