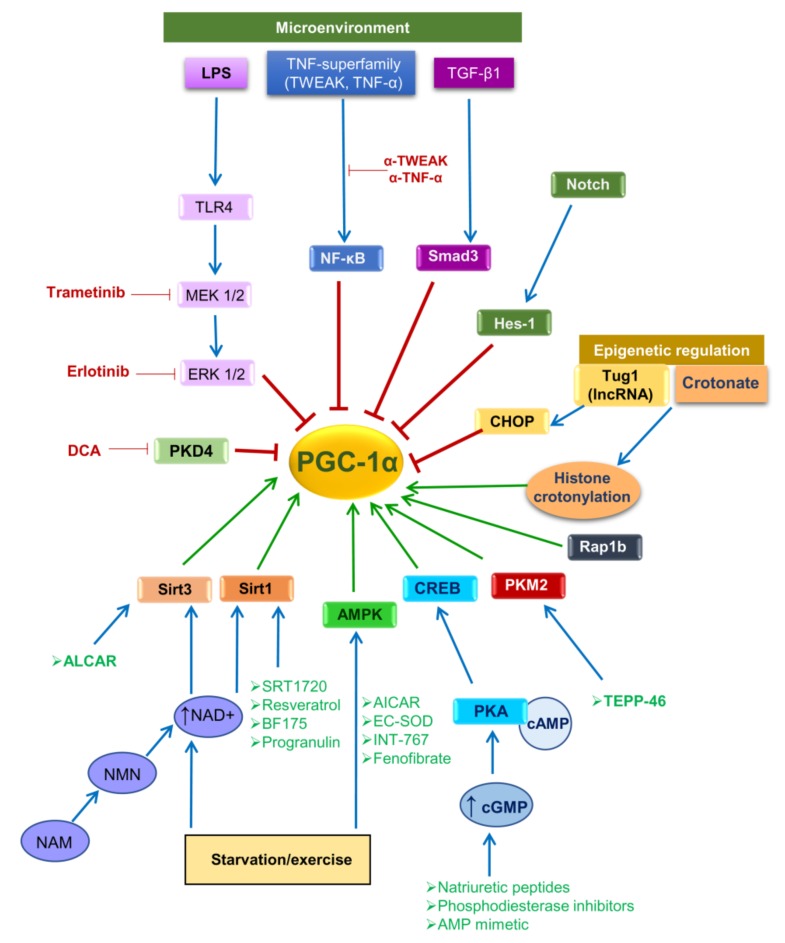
Figure 2.
Regulators of PGC-1α gene expression, activity and potential for therapeutic intervention aimed at increasing PGC-1α activity. The microenvironment (including mediators of inflammation and fibrosis), starvation/exercise and epigenetic regulation are the main modulators of PGC-1α activity. These, in turn, modulate intracellular signaling pathways that negatively (red lines) or positively (green lines) regulate PGC-1α gene expression and activity. Therapeutic approaches potentially upregulating PGC-1α gene expression and activity are depicted outside boxes: in green, those that activate specific intracellular signaling pathways to increase PGC-1α activity, and in red, those that inhibit specific intracellular signaling pathways to promote PGC-1α activity. Abbreviations: AICAR: 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-d-ribofuranoside, ALCAR: antioxidant agent acetyl-l-carnitine, AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase, cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cGMP: cyclic guanosine monophosphate, CHOP: C/EBP homologous protein, CREB: cAMP responsive element binding protein, DCA: dichloroacetate, ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase, LPS: lipopolysaccharide, MEK: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, NAD: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, NAM: niacinamide, NF-κB: nuclear factor κB, NMN: nicotinamide mononucleotide, PDK4: pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4, PKA: protein kinase A, PKM2: pyruvate kinase M2, Rap1b: RAS-Related Protein Rap1b, Sirt1: sirtuin 1, Sirt3: sirtuin 3, TEPP-46: tetraethyl diphosphate 46, TGF-β1: transforming growth factor β1, TLR4: toll-like receptor 4, TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α, Tug1: taurine up-regulated gene 1, TWEAK: TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis.