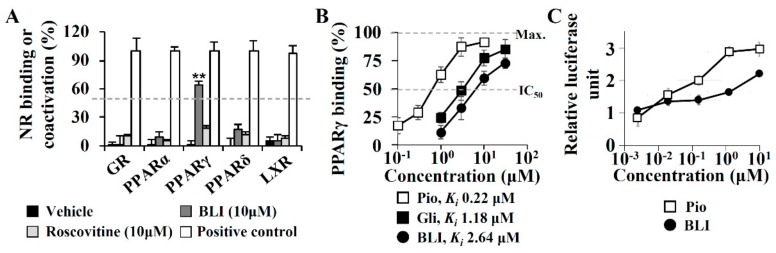
Figure 3.
Molecular target identification of butyrolactone I. (A) Competitive time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer (TR-FRET)-based nuclear receptor (glucocorticoid receptor (GR), PPAR subtype α/γ/δ, and iver X receptor (LXR)) binding assay was performed for butyrolactone I and roscovitine. (B) Ki values for PPARγ binding were calculated by the Cheng and Prusoff equation. Pioglitazone (pio) and glibenclamide (gli) were used as positive controls. (C) Cell-based PPARγ luciferase reporter transactivation assay was performed. HEK293T cell was co-transfected with an expression vector encoding full length PPARγ, a reporter vector encoding the firefly luciferase following PPARγ response element (PPRE), and a normalization vector encoding the Renila luciferase. After the treatment of the compounds including the butyrolactone I for 20 h to the cells, the signals of luminescence were detected and normalized. Values represent means ± SD (n = 3); * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01. IC50: half-maximum inhibition concentrations.