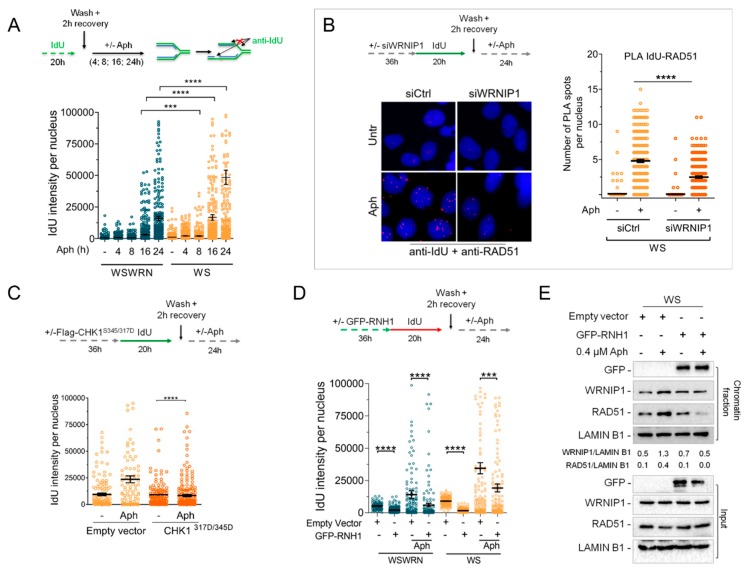
Figure 6.
RAD51-ssDNA association requires WRNIP1 in WS cells upon MRS. (A) Detection of ssDNA by IF with an anti-BrdU/IdU antibody in WSWRN and WS cells treated with 0.4 µM Aph for different times as reported in the scheme. Graph shows the mean ± SE from three independent experiments; (B) Analysis of proximity between ssDNA (anti-BrdU/IdU antibody) and endogenous RAD51 (anti-RAD51 antibody) performed by in situ PLA assay in WS cells depleted of WRNIP1 and treated as reported in the scheme. PLA interaction is shown in red. Graph shows the number of PLA spots per nucleus; (C) Detection of ssDNA by IF with anti-BrdU/IdU antibody in WS cells transfected with an empty vector or a FLAG-tagged CHK1317/345D and treated with 0.4 µM Aph. Graph shows the mean ± SE from three independent experiments; (D) Detection of ssDNA by IF with anti-BrdU/IdU antibody in WSWRN or WS cells treated as reported in the scheme after transfection with a plasmid expressing GFP-tagged RNaseH1. Graph shows the mean ± SE from three independent experiments; (E) WB analysis of chromatin binding of WRNIP1 and RAD51 in WS cells treated as in (D). Chromatin fractionation was performed as described in Figure 2A. The membrane was probed with the indicated antibodies. The normalized ratio of the chromatin-bound WRNIP1/LAMIN B1 or RAD51/LAMIN B1 are given.