Table 1.
Monoterpenes with gastroprotective and healing effects.
| Compound | Experimental Model: Treatment (Acute or Chronic) and Doses | Effect | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ascaridole [50] 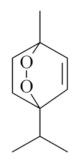
|
NSAID - Acute *10 mg/kg (p.o.) ~ ↓ 52% *20 mg/kg (p.o.) ~ ↓ 44% |
Gastroprotective and healing effects | ↓Acid secretion (↑pH) ↓ Pepsin |
|
Acetic Acid (20 %) - Chronic (7 days): 20 mg/kg (p.o.) - ↓ 57% | |||
| Vehicle: Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose | |||
| Citral [45] 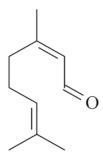
|
NSAID – Acute 25 mg/kg (p.o.) - ↓ 74.0% 100 mg/kg (p.o.) - ↓ 35.0%300 mg/kg (p.o.) - ↓ 48.0 % |
Gastroprotective effect | |
| Vehicle: Tween 80 - 1% | |||
| Eucalyptol or 1,8-Cineole [51] 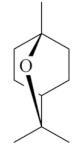
|
NSAID – Acute 50 mg/kg (p.o.) - ↓ 58.2% 100 mg/kg (p.o.) - ↓ 61.2% 200 mg/kg (p.o.) - ↓ 74.1% |
Gastroprotective and healing effect | ↑ Mucus (89.3%), ↑SH, ↓LPO and ↓MPO |
|
Absolute Ethanol - Acute 50 mg/kg (p.o.) - ↓ 88.1% 100 mg/kg (p.o.)- ↓ 98.5% 200 mg/kg (p.o.)- ↓ 99.2% |
↑ Cell proliferation | ||
|
Acetic Acid (30%) - Chronic (14 days) 100 mg/kg (p.o.)- ↓ 43.1% |
|||
| Vehicle: Tween 80 - 1% | |||
| Epoxy-carvone [52] 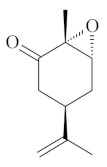
|
NSAID - Acute 10 mg/kg (p.o.) – ↓ 60.4 % 30 mg/kg (p.o.) – ↓ 47.9 % 50 mg/kg (p.o.) – ↓ 62.7 % Absolute Ethanol - Acute 10 mg/kg (p.o.) - ↓ 77.7% 30 mg/kg (p.o.) - ↓ 69.2% 50 mg/kg (p.o.) - ↓ 61.4% Vehicle: Tween 80 - 5% |
Gastroprotective effect | |
| Linalool [53,54,55] 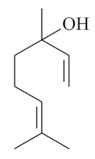
|
Ethanol 90% - acute: 33 mg/kg (p.o.) - ↓ 56.0% Vehicle: methylcellulose 0.1% |
Gastroprotective effect | |
|
Absolute Ethanol - acute: 10 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓ 85.5% 20 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓ 76.2% 40 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓ 89.3% |
|||
|
Acetic Acid (80%) - chronic (14 days): 40 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓ 48.0% |
Gastroprotective and healing effects | ↓MPO and ↓ LPO | |
| Vehicle: Saline | |||
| Linalyl acetate [55] 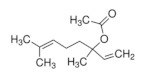
|
Ethanol 90% - acute: 36 mg/kg (p.o.) - ↓49.0% Vehicle: methylcellulose 0.1% |
Gastroprotective effect | |
| Menthol [56,57] 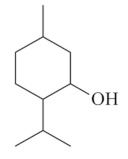
|
NSAID - Acute: 50 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓ 73.0 % |
Gastroprotective effect | ↓ Acid secretion ↑ Mucus and PGE2 ↑ Compounds SH |
|
Absolute Ethanol - Acute: 50 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓ 88.6–92.0% 100 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓ 98.4% |
↑ ATP-sensitive potassium channel | ||
| Vehicle: Tween 80 - 8% | ↓ MPO,↑ GSH, ↑GSH-Px, ↑GR ↓ TNF-α, ↓ IL-6,↑IL-10 Anti-apoptotic effect (HSP-70, Bax) |
||
| Myrtenol [58] 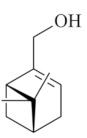
|
Absolute Ethanol - Acute: 25 mg/kg (p.o)- ↓ 40.2% 50 mg/kg (p.o)- ↓ 83.0% 100 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓ 83.2% |
Gastroprotective effect | Activation of GABA-A receptors ↓ LPO |
| Vehicle: Tween 80 - 2% | |||
| Nerol [59] 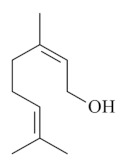
|
Absolute Ethanol - acute: *10 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓~94% *30 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓~82% *100 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓~92% *300 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓~94% Vehicle: Tween 80 - 0.5% |
Gastroprotective effect | |
| α-pinene [60] 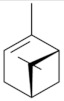
|
Absolute Ethanol - Acute: 10 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓ 48.6% 30 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓ 43.9% 100 mg/kg (p.o) - ↓ 42.1% Vehicle: Tween 80 - 0.1% |
Gastroprotective effect | ↓ Acid secretion ↑ Mucus |
| α-terpineol [61] 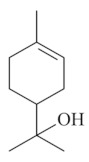
|
NSAID - Acute: 30 mg/kg (p.o)- ↓ 63.9% 50 mg/kg (p.o)- ↓ 81.3% Ethanol 70% - Acute: 10 mg/kg (p.o)- ↓ 66.7% 30 mg/kg (p.o)- ↓ 81.0% 50 mg/kg (p.o)- ↓ 94.1% Vehicle: Tween 80 - 10% |
Gastroprotective effect | |
| Thymoquinone [62] 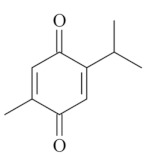
|
NSAID - Acute: * 20 mg/kg (p.o) - ~↓ 46% |
↑ SOD, ↑GPx, ↑NO, ↓ apoptosis |
|
| Vehicle: Corn oil 10% | ↓iNOS,↓TOS, ↓OSI, ↓ NF-κβ, ↓ TNF-α, ↑TAS, ↑TT, ↑ADMA, ↑ DDAH-1, ↑DDAH-2 |
ADMA—asymmetric dimethylarginine; DDAH-1—dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1; DDAH-2—dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-2; GPx—glutathione peroxidase; IL-10—interleukin 10; MIC—minimal inhibitory concentration; MMP-9—matrix metalloproteinase-9; MPO—myeloperoxidase; NF-κB; nuclear factor kappa B; NO—nitric oxide; NSAID—non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; OSI—oxidative stress index; P.O.—administered by oral route; PGE2—prostaglandin E2; SH—sulfhydryl compounds; SOD—superoxide dismutase; TAS—total antioxidant status; TNF-α—tumor necrosis factor-α; TOS—Total oxidant status and TT—total thiol.* This data was estimated on the basis of results presented in the article.
