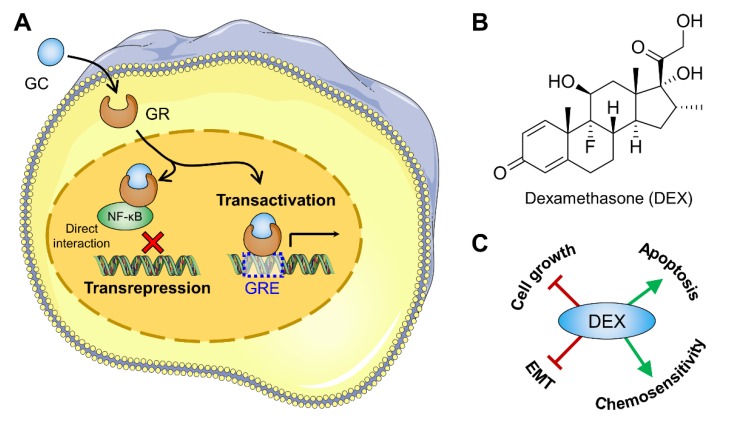
Figure 1.
(A) Sketch showing the genomic actions of glucocorticoids (GCs) such as dexamethasone (DEX). When bound to DEX, the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) complex translocates into the nucleus and modifies the synthesis of several metabolic proteins. This is done either through directly binding to glucocorticoid response elements (GREs) on the DNA or through influencing the activity of transcription factors (i.e., nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B-cells, NF-κB); (B) Chemical structure of DEX; (C) Described effects of DEX on cancer cells. Parts of the figure are drawn using pictures from Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com), licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0).