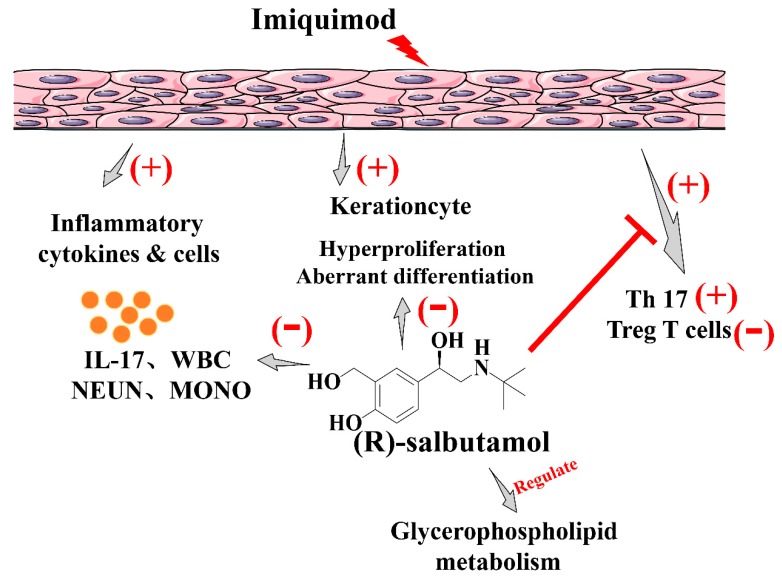
Figure 9.
Schematic diagram showing possible mechanisms responsible for the pharmacological efficacy of (R)-salbutamol. Oral administration of (R)-salbutamol markedly reduced the plasma levels of IL-17, decreased the proportion of CD4+ Th17+ T cells (Th17) whereas increased the percentage of CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the spleens, and affected glycerophospholipid metabolism.