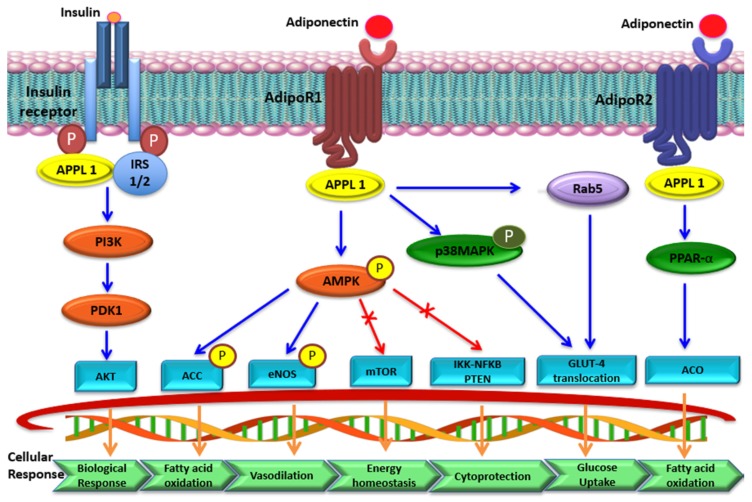
Figure 3.
Key signaling pathways of adiponectin. Adiponectin and AdipoRs (AdipoR1 and AdipoR2) interact to activate downstream signaling pathways. Binding of adiponectin to its receptors activates adaptor protein APPL1. Activated APPL1 initiates complex signal transduction by activating PPAR-α and phosphorylating AMPK and p38-MAPK. Phospho-AMPK inhibits lipogenesis and promotes fatty acid oxidation and transport into the mitochondria by phosphorylating ACC-1. Phosphorylated eNOS stimulates nitric oxide (NO), which results in vasodilation. In addition, adiponectin shows cytoprotective effect because activation of AMPK suppresses mTOR and IKK-NF-κB-PTEN signaling. Metabolic effects of insulin are mainly controlled by PI3K-Akt signaling. As PI3K-Akt is activated, glycogen synthesis and glucose uptake increases but lipolysis is suppressed. Insulin sensitivity increases when IRS1/2 is activated by adiponectin.