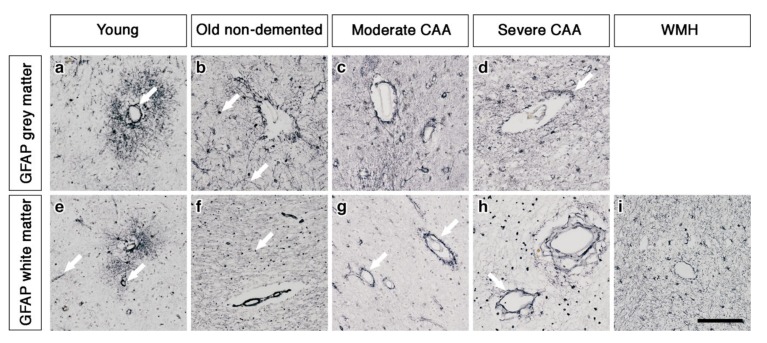
Figure 2.
The pattern of immunostaining for GFAP associated with the blood vessels of grey and white matter. In young brains, GFAP immunostaining reveals highly arborized astrocytes and profiles of blood vessels of all sizes in both grey and white matter (arrows) (a and e). In old non-demented brains, the GFAP immunostaining appears intense in the grey matter, highlighting fine processes and cell bodies (arrow) (b) but granular (arrow) and mostly in perivascular locations in the white matter (f). In the grey matter of moderate CAA brains, the immunostaining of GFAP shows intensely stained processes surrounding the vessels (c) but in the white matter is confined to the perivascular locations (arrows) (g). In severe CAA brains, GFAP immunostaining is intense and localised to the blood vessels of both grey (arrow) (d) and white matter (arrow) (h) with small cell bodies also present in the white matter (h). In WMH brains the GFAP immunostaining is relatively intense, highlighting fine processes and cell bodies in the white matter and surrounding vessels (i). Scale bar 100 µm.